This is “Politics in the United States”, section 10.2 from the book Sociology: Brief Edition (v. 1.1). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
10.2 Politics in the United States
Learning Objectives
- Understand what political ideology is and how it is measured.
- List the correlates of political participation.
- Discuss the controversy over political lobbying.
The discussion of theories of power and society began to examine the U.S. political system. Let’s continue this examination by looking at additional features of U.S. politics. We start with political ideology and political parties.
Political Ideology and Political Parties
Two central components of modern political systems are (a) the views that people hold of social, economic, and political issues and (b) the political organizations that try to elect candidates to represent those views. We call these components political ideology and political parties, respectively.
Political Ideology
Political ideologyViews on social, political, and economic issues. is a complex concept that is often summarized by asking people whether they are liberal or conservative. For example, the GSS asks, “I’m going to show you a seven-point scale on which the political views that people might hold are arranged from extremely liberal to extremely conservative. Where would you place yourself on this scale?” For convenience’ sake, responses to this question in the 2008 GSS are grouped into three categories—liberal, moderate, and conservative—and displayed in Figure 10.5 "Political Ideology". We see that moderates slightly outnumber conservatives, who in turn outnumber liberals.
Figure 10.5 Political Ideology
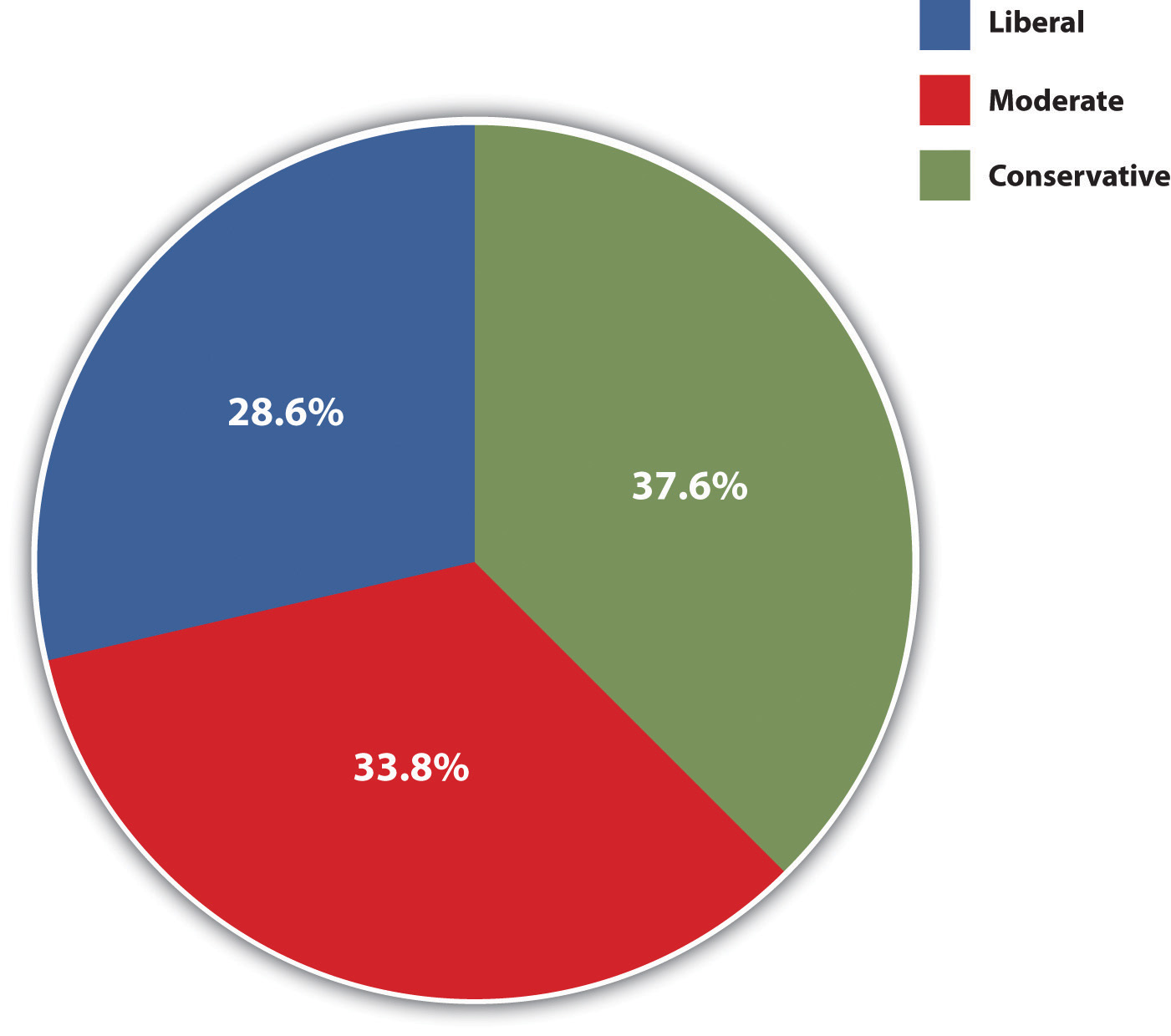
Source: Data from General Social Survey, 2010.
This is a common measure of political ideology, but social scientists often advise using a series of questions to measure political ideology, which consists of views on at least two sorts of issues, social and economic. Social issues concern the morality of behavior and are similar to those we examined in the previous chapter’s section on aging and conservatism. Economic issues, on the other hand, concern such things as taxes and the distribution of income and wealth. People can hold either liberal or conservative attitudes on both types of issues, but they can also hold mixed attitudes: liberal on social issues and conservative on economic ones, or conservative on social issues and liberal on economic ones. Educated, wealthy people, for example, may want lower taxes (generally considered a conservative view) but also may favor abortion rights and oppose the death penalty (both considered liberal positions). In contrast, less educated, working-class people may favor higher taxes for the rich (a liberal view, perhaps) but oppose abortion rights and favor the death penalty.
We also see mixed political ideologies when we look at African Americans’ and whites’ views on social and economic issues. African Americans tend to be more conservative than whites on social issues but more liberal on economic concerns. This tendency is depicted in Figure 10.6 "Race and Attitudes on Social and Economic Issues", which shows responses to GSS questions on whether premarital sex is wrong, a social issue, and on whether the government should reduce income differences between the rich and poor, an economic issue. African Americans are more likely than whites to take a conservative view on the social issue by thinking that premarital sex is wrong but are more likely to take a liberal view on the economic issue by thinking that the government should reduce income inequality.
Figure 10.6 Race and Attitudes on Social and Economic Issues
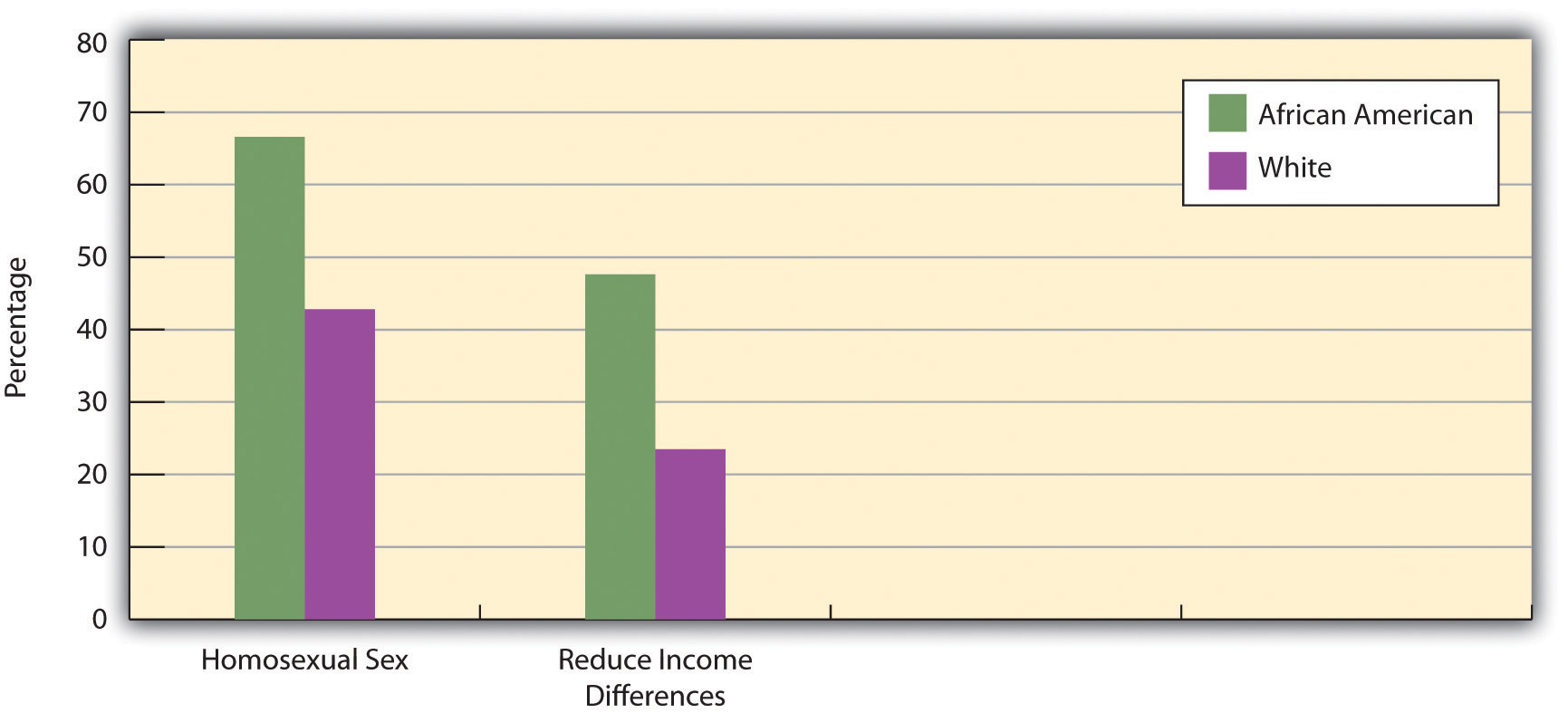
Percentage saying that homosexual sex is always wrong and percentage saying that government should reduce income differences.
Source: Data from General Social Survey, 2010.
Political Parties
People’s political ideologies often lead them to align with a political partyAn organization that supports particular political positions and tries to elect candidates to office to represent those positions., or an organization that supports particular political positions and tries to elect candidates to office to represent those positions. The two major political parties in the United States are, of course, the Democratic and Republican parties. However, in a national poll in May 2011, 32% of Americans called themselves Independents, compared to 36% who called themselves Democrats and only 24% who called themselves Republicans. The number of Americans who consider themselves Independents, then, almost equals the number who consider themselves Democrats and exceeds the number who consider themselves Republicans (Dao & Sussman, 2011).Dao, J., & Sussman, D. (2011, May 5). For Obama, big rises in poll numbers after Bin Laden. The New York Times, p. A1.
Figure 10.7

The number of Americans who call themselves political independents almost equals the number who consider themselves either a Democrat or a Republican.
© Thinkstock
An important question for U.S. democracy is how much the Democratic and Republican parties differ on the major issues of the day. The Democratic Party is generally regarded as more liberal, while the Republican Party is regarded as more conservative, and voting records of their members in Congress generally reflect this difference. However, some critics of the U.S. political system think that in the long run there is not a “dime’s worth of difference,” to quote an old saying, between the two parties, as they both ultimately work to preserve corporate interests and capitalism itself (Alexander, 2008).Alexander, S. A. (2008, January 10). Socialists emerging as Democrats, Republicans lose voter confidence. American Chronicle. Retrieved from http://www.americanchronicle.com/articles/ view/48507 In their view, the Democratic Party is part of the problem, as it tries only to reform the system instead of bringing about the far-reaching changes said to be needed to achieve true equality for all. These criticisms notwithstanding, it is true that neither of the major U.S. parties is as left-leaning as some of the major ones in Western Europe. The two-party system in the United States may encourage middle-of-the road positions, as each party is afraid that straying too far from the middle will cost it votes. In contrast, because several Western European nations have a greater number of political parties, a party may feel freer to advocate more polarized political views (Muddle, 2007).Muddle, C. (2007). Populist radical right parties in Europe. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Some scholars see this encouragement of middle-of-the-road positions (and thus political stability) as a benefit of the U.S. two-party system, while other scholars view it as a disadvantage because it limits the airing of views that might help a nation by challenging the status quo (Richard, 2010).Richard, J. (2010, May 29). One cheer for the two-party system. OpEdNews. Retrieved from http://www.opednews.com/articles/One-Cheer-for-the-Two-Part -by-Jerome-Richard-100527-148.html One thing is clear: in the U.S. two-party model, it is very difficult for a third party to make significant inroads, because the United States lacks a proportional representation system, found in many other democracies, in which parties win seats proportional to their share of the vote (Disch, 2002).Disch, L. J. (2002). The tyranny of the two-party system. New York, NY: Columbia University Press. Instead, the United States has a winner-takes-all system in which seats go to the candidates with the most votes. Even though the Green Party has several million supporters across the country, for example, its influence on national policy has been minimal, although it has had more influence in a few local elections.
Whether or not the Democratic and Republican parties are that different, U.S. citizens certainly base their party preference in part on their own political ideology. Evidence of this is seen in Figure 10.8 "Political Ideology and Political Party Preference", which shows the political ideology of GSS respondents who call themselves Democrats or Republicans. People’s political ideology is clearly linked to their party preference.
Figure 10.8 Political Ideology and Political Party Preference
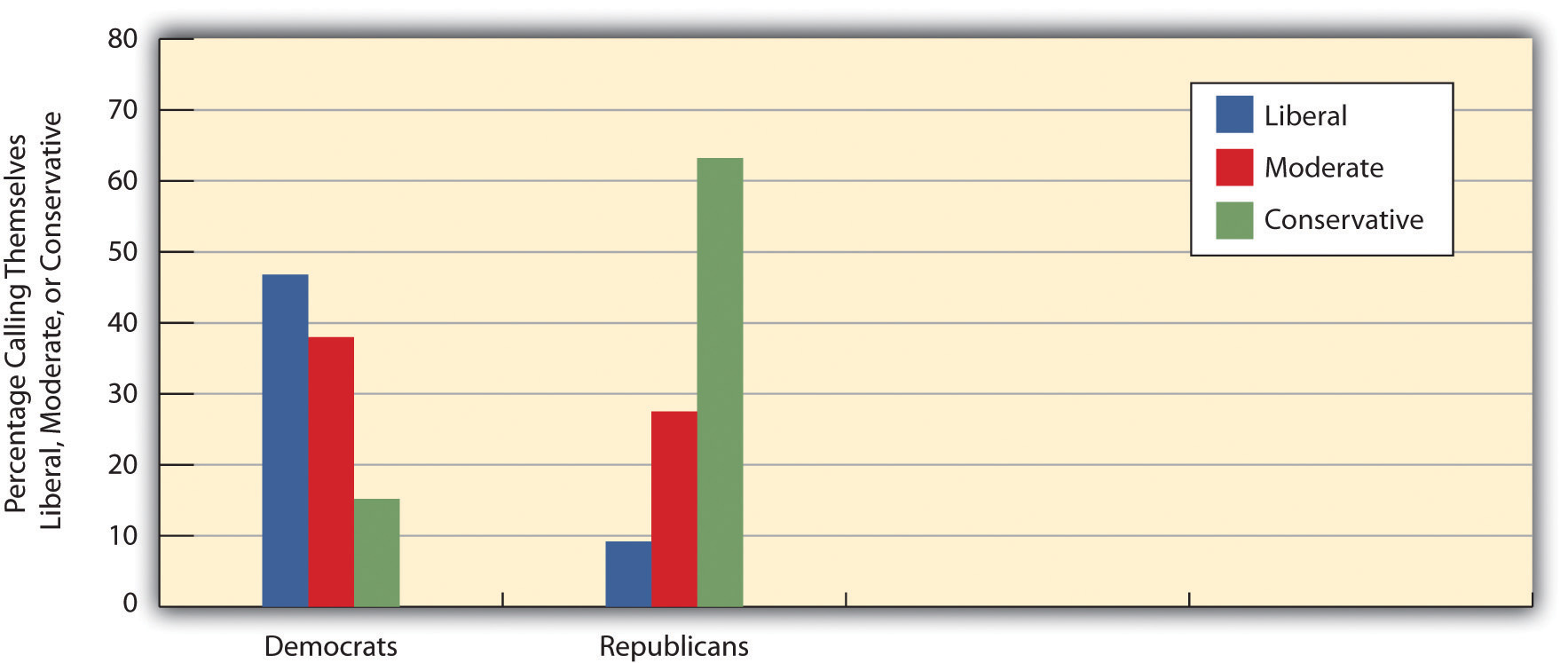
Source: Data from General Social Survey, 2010.
Political Participation
Perhaps the most important feature of representative democracies is that people vote for officials to represent their views, interests, and needs. For a democracy to flourish, political theorists say, it is essential that “regular” people participate in the political process. The most common type of political participation, of course, is voting; other political activities include campaigning for a candidate, giving money to a candidate or political party, and writing letters to political officials. Despite the importance of these activities in a democratic society, not very many people take part in them. Voting is also relatively uncommon among Americans, as the United States ranks lower than most of the world’s democracies in voter turnout (International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance, 2009)International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance. (2009). Voter turnout. Retrieved from http://www.idea.int/vt/index.cfm.
Not only is U.S. voter turnout relatively low in the international sphere, but it has also declined since the 1960s (see Figure 10.9 "Trends in Voter Turnout in Nonpresidential Election Years"). One factor that explains these related trends is voter apathy, prompted by a lack of faith that voting makes any difference and that government can be helpful. This lack of faith is often called political alienationA lack of faith that voting makes any difference and that government can be helpful.. As Figure 10.10 "Trust in U.S. Government" dramatically shows, lack of faith in the government has dropped drastically since the 1960s, thanks in part, no doubt, to the Vietnam War during the 1960s and 1970s and the Watergate scandal of 1970s.
Figure 10.9 Trends in Voter Turnout in Nonpresidential Election Years
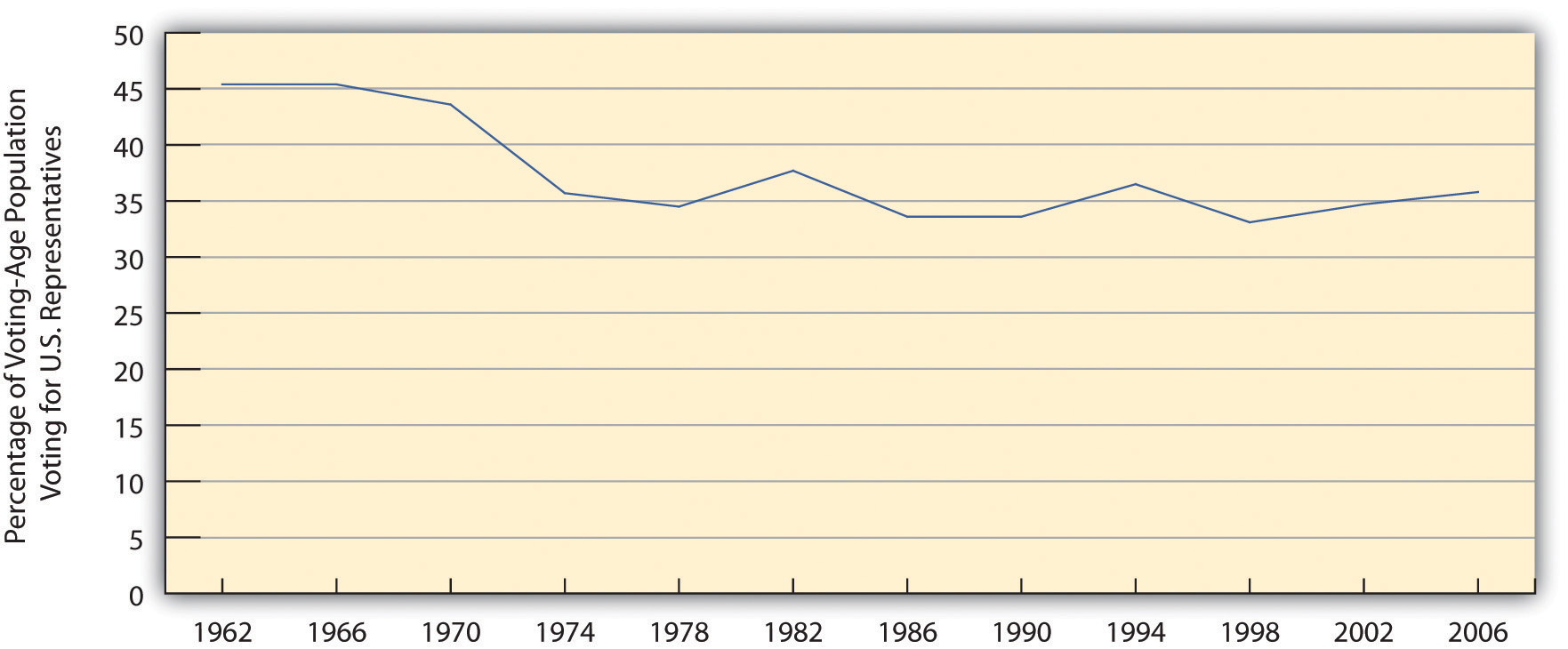
Source: Data from U.S. Census Bureau. (2009). Statistical abstract of the United States: 2009. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab.
Figure 10.10 Trust in U.S. Government
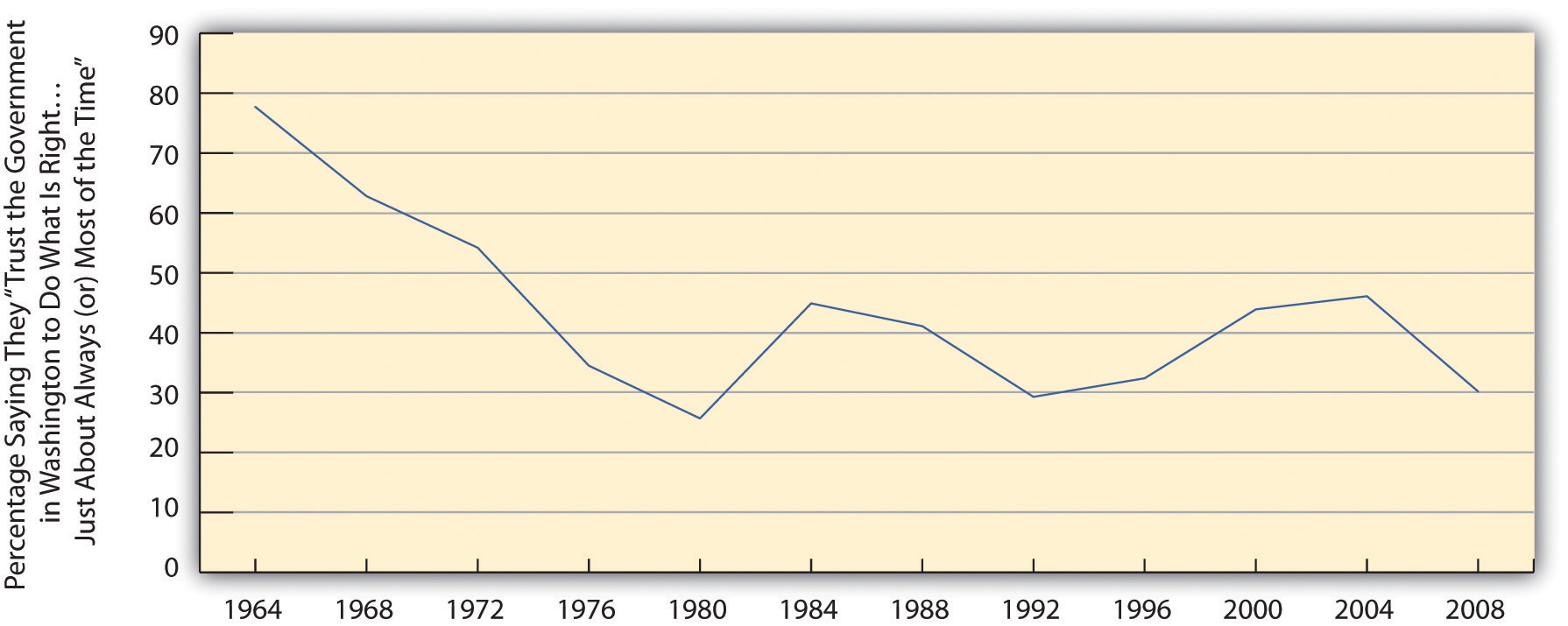
Source: American National Election Study.
Yet it is also true that voter turnout varies greatly among Americans. In general, several sets of factors make citizens more likely to vote and otherwise participate in the political process (Burns, Schlozman, & Verba, 2001).Burns, N., Schlozman, K. L., & Verba, S. (2001). The private roots of public action: Gender, equality, and political participation. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. These factors, or correlates of political participation, include (a) high levels of resources, including time, money, and communication skills; (b) psychological engagement in politics, including a strong interest in politics and a sense of trust in the political process; and (c) involvement in interpersonal networks of voluntary and other organizations that recruit individuals into political activity. Thus people who are, for example, wealthier, more interested in politics, and more involved in interpersonal networks are more likely to vote and take part in other political activities than those who are poorer, less interested in politics, and less involved in interpersonal networks. Reflecting these factors, age and high socioeconomic status are especially important predictors of voting and other forms of political participation, as citizens who are older, wealthier, and more educated tend to have more resources, to be more interested in politics and more trustful of the political process, and to be more involved in interpersonal networks. As a result, they are much more likely to vote than people who are younger and less educated (see Figure 10.11 "Age, Education, and Percentage Voting, 2008").
Figure 10.11 Age, Education, and Percentage Voting, 2008
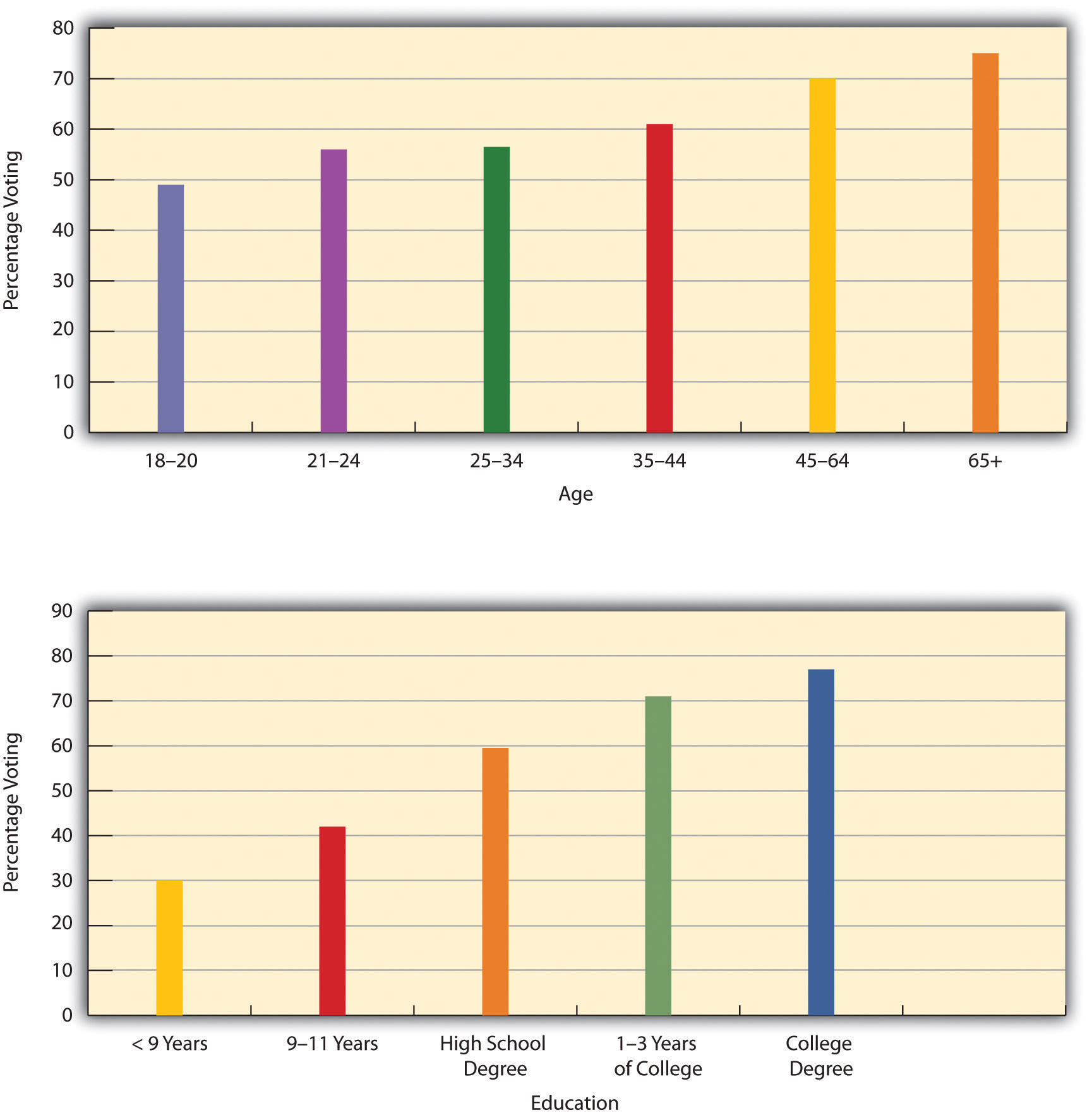
Source: U.S. Census Bureau. (2009). Statistical abstract of the United States: 2009. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab.
The lower voting rates for young people might surprise many readers: because many college students are politically active, it seems obvious that they should vote at high levels. That might be true for some college students, but the bulk of college students are normally not politically active, because they are too busy with their studies, extracurricular activities, and/or work, and because they lack sufficient interest in politics to be active. It is also true that there are many more people aged 18 to 24 (about 30 million), the traditional ages for college attendance, than there are actual college students (11 million). In view of these facts, the lower voting rates for young people are not that surprising after all.
Race and ethnicity also influence voting. In particular, Asians and Latinos vote less often than African Americans and whites among the citizen population. In 2008, roughly 65% of African Americans and 66% of non-Latino whites voted, compared to only 48% of Asians and 50% of Latinos (File & Cressey, 2010).File, T., & Cressey, S. (2010). Voting and registration in the election of November 2008 (Current Population Report P20–562). Washington, DC: U.S. Census Bureau. The voting percentage for African Americans and Latinos was the highest for these groups since the Census Bureau began measuring citizens’ voting in 1996, possibly because of the presence of Barack Obama, who considers himself an African American, on the Democratic ticket.
The impact of age, race and ethnicity, education, and other variables on voting rates provides yet another example of the sociological perspective. As should be evident, they show that these aspects of our social backgrounds affect a very important political behavior, voting, even if we are not conscious of this effect.
Special-Interest Groups and Lobbying: The Influence Industry
From 2003 through 2008, political action committees (PACs)An organization formed by special-interest groups to raise and spend money on behalf of political campaigns and various political issues., organizations formed by special-interest groups to raise and spend money on behalf of political campaigns and various political issues, contributed more than $1 billion to the election campaigns of candidates for Congress (U.S. Census Bureau, 2009).U.S. Census Bureau. (2009). Statistical abstract of the United States: 2009. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab In 2008 and 2009, special-interest groups spent more than $6.3 billion to lobby Congress, the White House, and various federal agencies. They employed some 14,000 lobbyists, who outnumbered members of Congress 27 to 1, on such issues as health care, military spending, and transportation (Center for Responsive Politics, 2009).Center for Responsive Politics. (2009). Lobbying database. Retrieved from http://www.opensecrets.org/lobbyists The top lobbying group in 2009 was the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, which spent more than $65 million to lobby Congress, federal agencies, and other parties; in second place was Exxon Mobil, which spent more than $21 million. The pharmaceutical and health products industry as a whole spent more than $200 million in 2009, while the insurance industry spent $122 million, oil and gas companies $121 million, electric and gas utilities $108 million, and business associations $93 million.
Figure 10.12

The U.S. Chamber of Commerce and other lobbying groups spent more than $6.3 billion in 2008 and 2009 on their efforts to influence federal legislation and regulations.
© Thinkstock
Dubbed the “influence industry,” these lobbying efforts have long been criticized as having too much impact on federal policy and spending priorities. It is logical to think that the influence industry spends these large sums of money because it hopes to affect key legislation and other policies. This expenditure raises an important question: are PACs, special-interest groups, and lobbying good or bad for democracy? This question goes to the heart of the debate between pluralist and elite theories, discussed earlier. Representatives of PACs and lobbying groups say it is important that elected officials hear all possible views on complex issues and that these organizations merely give money to help candidates who already think a certain way. Supporting this notion, public officials say they listen to all sides before making up their minds and are not unduly influenced by the money they receive and by the lobbying they encounter. For their part, pluralist theorists say PACs and lobbying groups are examples of the competing veto groups favored by the pluralist model and that no one special-interest group wins out in the long run (James, 2004).James, M. R. (2004). Deliberative democracy and the plural polity. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas.
Critics of the influence industry say that its impact is both large and unwarranted and charge that PACs, lobbyists, and the special-interest groups that fund them are buying influence and subverting democracy. Ample evidence exists, they say, of the impact of the influence industry on which candidates get elected and on which legislation gets passed or not passed. While special-interest groups for various sides of an issue do compete with each other, they continue, corporations and their PACs are much better funded and much more influential than the groups that oppose them (Clawson, Neustadtl, & Weller, 1998; Cook & Chaddock, 2009).Clawson, D., Neustadtl, A., & Weller, M. (1998). Dollars and votes: How business campaign contributions subvert democracy. Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press; Cook, D. T., & Chaddock, G. R. (2009, September 28). How Washington lobbyists peddle power. The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved from http://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Politics/2009/0928/how-washington-lobbyists-peddle-power These concerns motivated sharp criticism of a U.S. Supreme Court decision in January 2010 regarding election advertisements by corporations and unions. The decision permitted corporations and unions to use money from their general funds to pay for ads urging the public to vote for or against a particular candidate. Because corporations have much more money than unions, the ruling was widely seen as being a procorporation one. The majority decision said that prohibitions of such advertising violated freedom of political speech by corporations and unions, while the minority decision said the ruling “threatens to undermine the integrity of elected institutions across the nation” (Vogel, 2010).Vogel, K. P. (2010, January 21). Court decision opens floodgates for corporate cash. Politico. Retrieved from http://www.politico.com/news/stories/0110/31786.html
Key Takeaways
- Political ideology consists of views on social issues and on economic issues. An individual might be liberal or conservative on both kinds of issues, or liberal on one kind of issue and conservative on the other kind.
- Almost as many Americans consider themselves Independents as consider themselves either Democrats or Republicans. Although some scholars say that there is not very much difference between the Democratic and Republican parties, liberals are more likely to consider themselves Democrats, and conservatives are more likely to consider themselves Republicans.
- Voting is the most common form of political participation. Several factors influence the likelihood of voting, and socioeconomic status (education and income) is a very important factor in this regard.
- Political lobbying remains a very controversial issue, and critics continue to charge that the “influence industry” has too much sway over American social and economic policy.
For Your Review
- Do you consider yourself to be politically conservative, moderate, or liberal? What are examples of some of your beliefs that lead you to define yourself in this manner?
- Do you think political lobbying is good or bad overall for the United States? Explain your answer.




