This is “Reactions of Amino Acids”, section 18.2 from the book Introduction to Chemistry: General, Organic, and Biological (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
18.2 Reactions of Amino Acids
Learning Objective
- Explain how an amino acid can act as both an acid and a base.
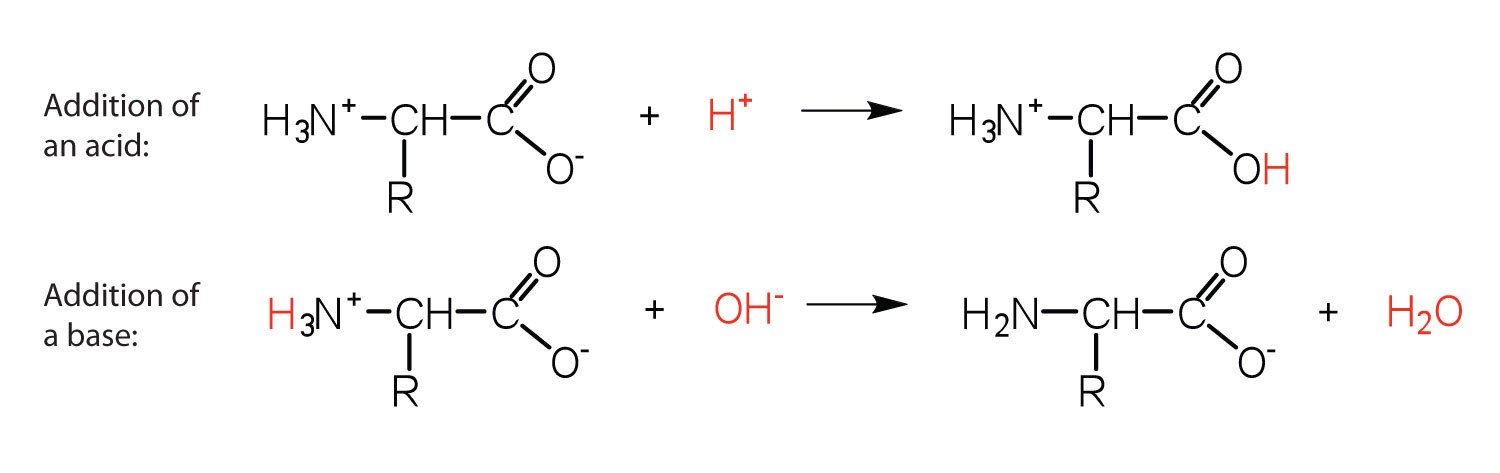
The structure of an amino acid allows it to act as both an acid and a base. An amino acid has this ability because at a certain pH value (different for each amino acid) nearly all the amino acid molecules exist as zwitterions. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen (H+) ion, and the amino acid becomes positively charged. If base is added, ion removal of the H+ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid. In both circumstances, the amino acid acts to maintain the pH of the system—that is, to remove the added acid (H+) or base (OH−) from solution.
Example 1
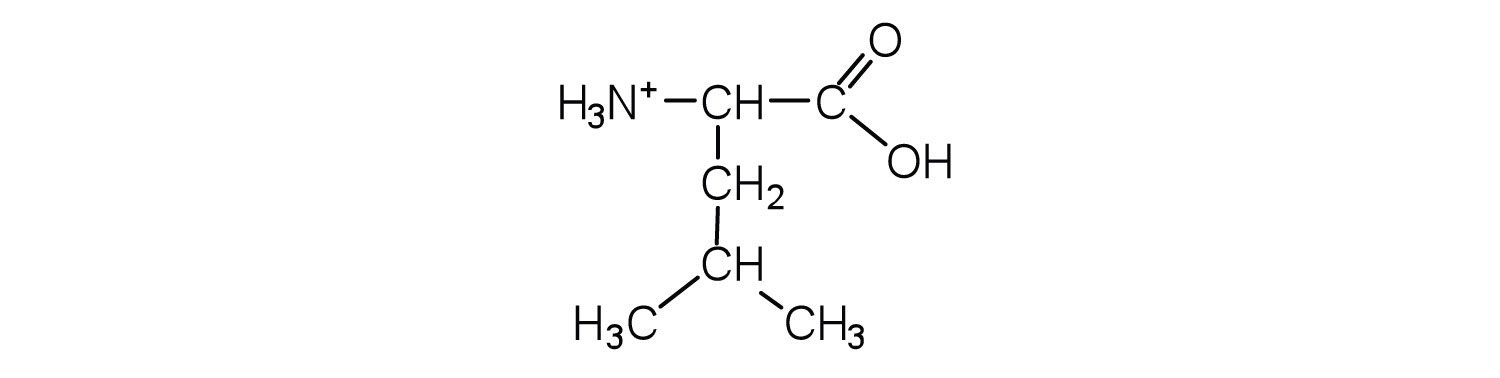
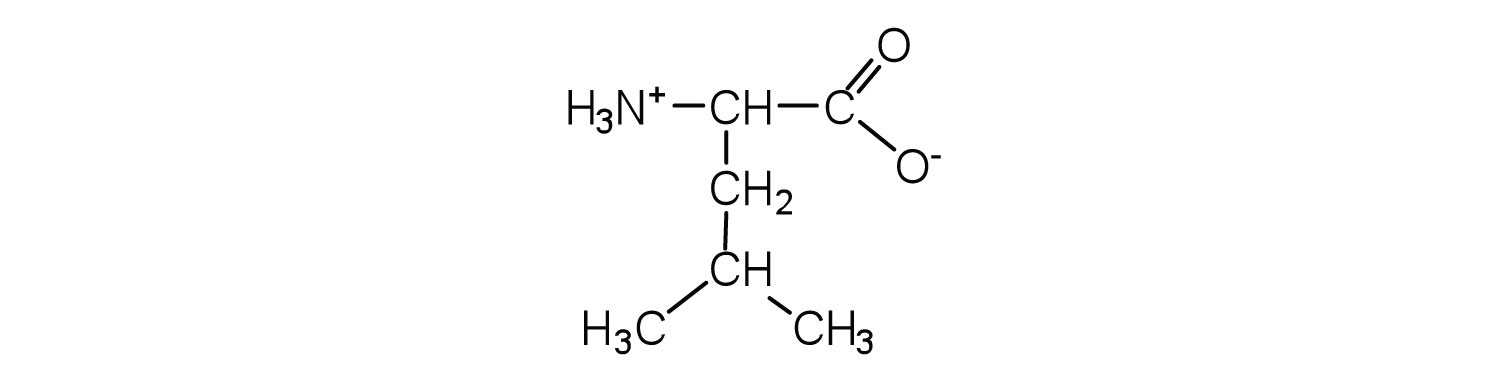
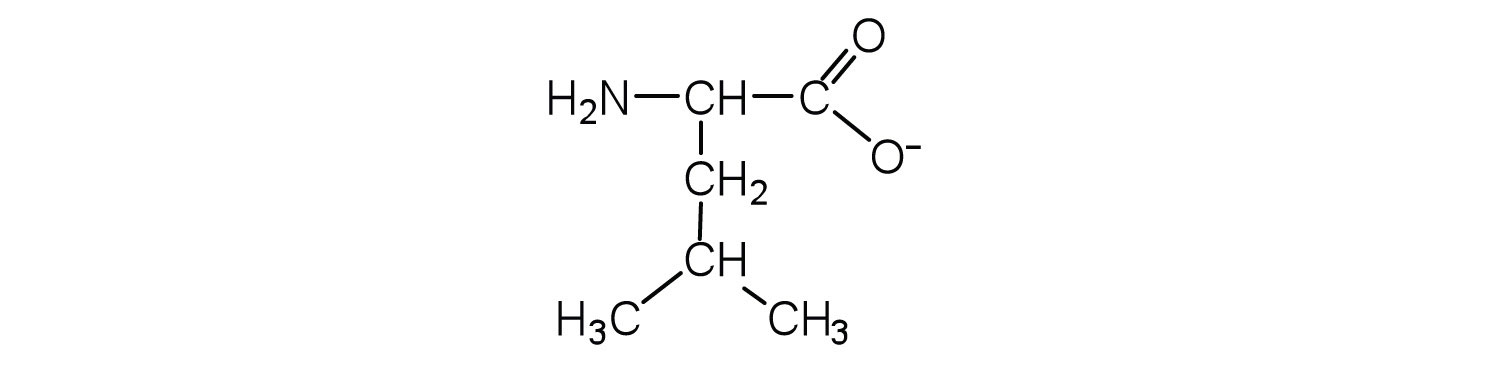
- Draw the structure for the anion formed when glycine (at neutral pH) reacts with a base.
- Draw the structure for the cation formed when glycine (at neutral pH) reacts with an acid.
Solution
-
The base removes H+ from the protonated amine group.
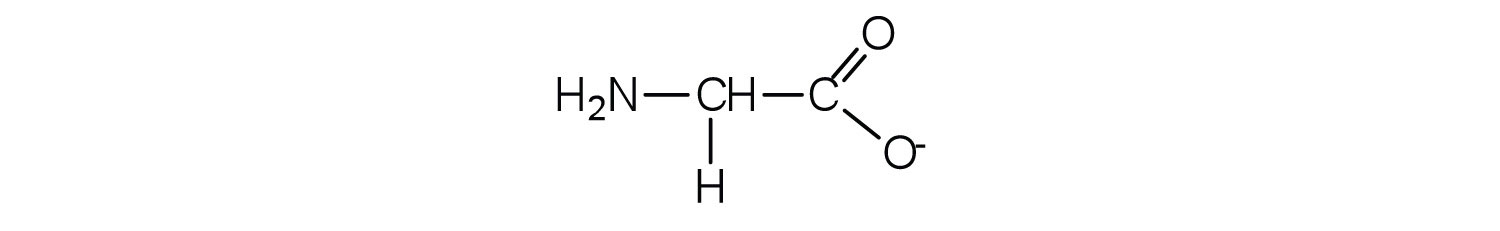
-
The acid adds H+ to the carboxylate group.
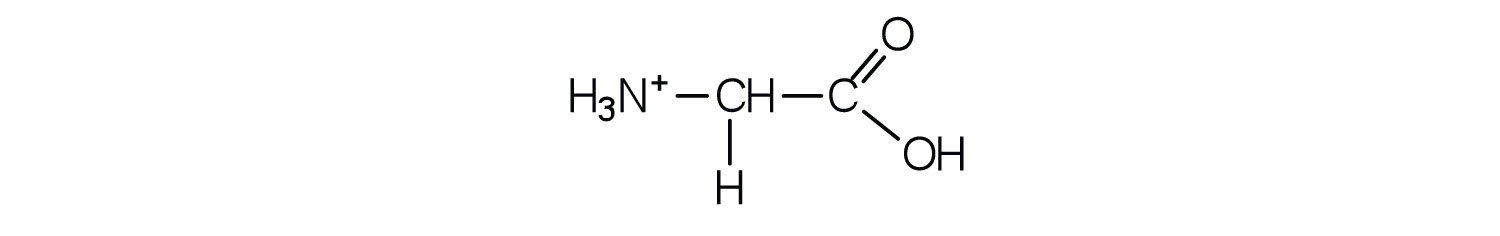
Skill-Building Exercise
-
Draw the structure for the cation formed when valine (at neutral pH) reacts with an acid.
-
Draw the structure for the anion formed when valine (at neutral pH) reacts with a base.
The particular pH at which a given amino acid exists in solution as a zwitterion is called the isoelectric pointThe pH at which a given amino acid exists in solution as a zwitterion. (pI). At its pI, the positive and negative charges on the amino acid balance, and the molecule as a whole is electrically neutral. The amino acids whose side chains are always neutral have isoelectric points ranging from 5.0 to 6.5. The basic amino acids (which have positively charged side chains at neutral pH) have relatively high pIs. Acidic amino acids (which have negatively charged side chains at neutral pH) have quite low pIs (Table 18.3 "pIs of Some Representative Amino Acids").
Table 18.3 pIs of Some Representative Amino Acids
| Amino Acid | Classification | pI |
|---|---|---|
| alanine | nonpolar | 6.0 |
| valine | nonpolar | 6.0 |
| serine | polar, uncharged | 5.7 |
| threonine | polar, uncharged | 6.5 |
| arginine | positively charged (basic) | 10.8 |
| histidine | positively charged (basic) | 7.6 |
| lysine | positively charged (basic) | 9.8 |
| aspartic acid | negatively charged (acidic) | 3.0 |
| glutamic acid | negatively charged (acidic) | 3.2 |
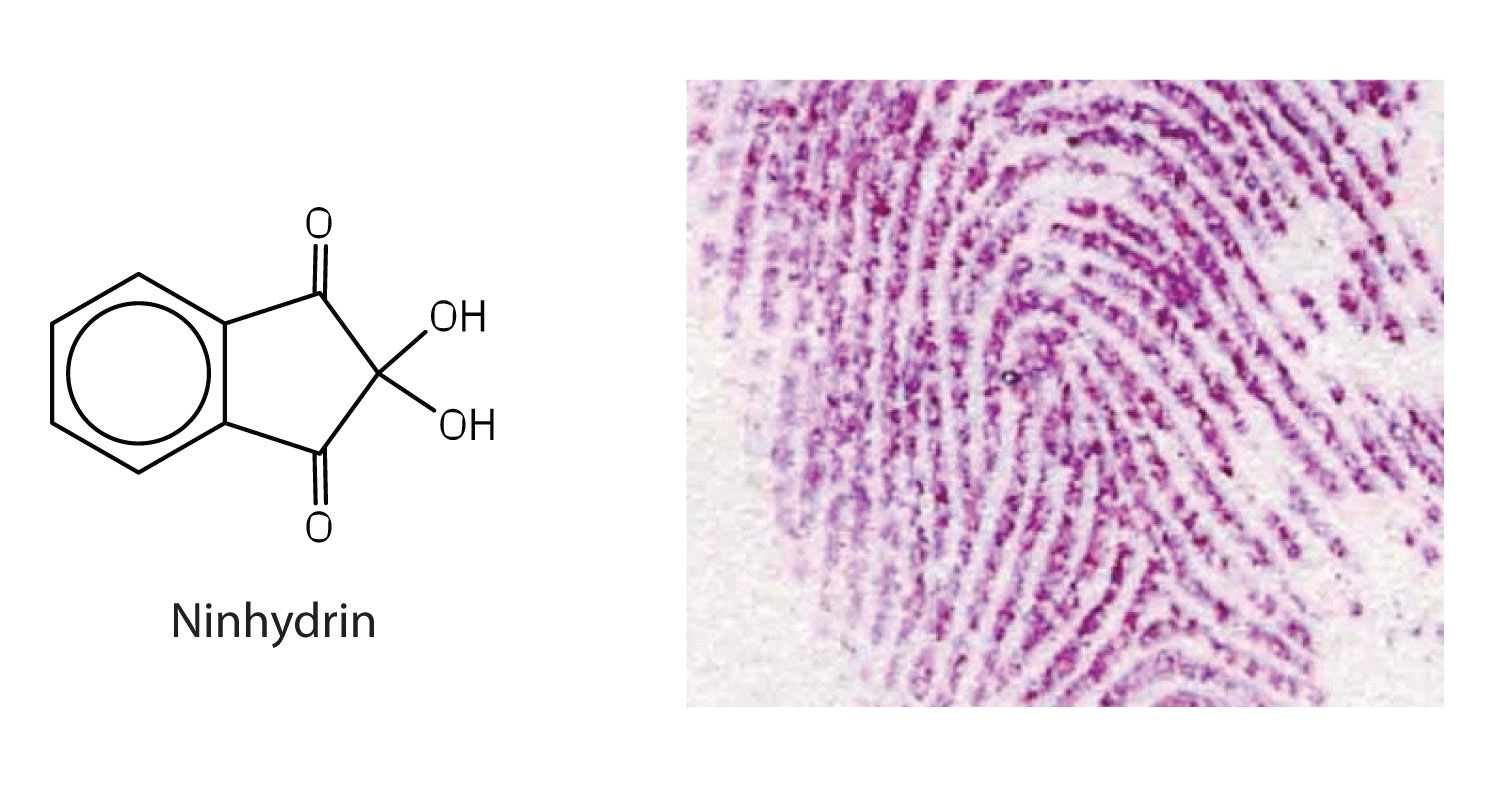
Amino acids undergo reactions characteristic of carboxylic acids and amines. The reactivity of these functional groups is particularly important in linking amino acids together to form peptides and proteins, as you will see later in this chapter. Simple chemical tests that are used to detect amino acids take advantage of the reactivity of these functional groups. An example is the ninhydrin test in which the amine functional group of α-amino acids reacts with ninhydrin to form purple-colored compounds. Ninhydrin is used to detect fingerprints because it reacts with amino acids from the proteins in skin cells transferred to the surface by the individual leaving the fingerprint.
Concept Review Exercises
-
Define each term.
- zwitterion
- isoelectric point
-
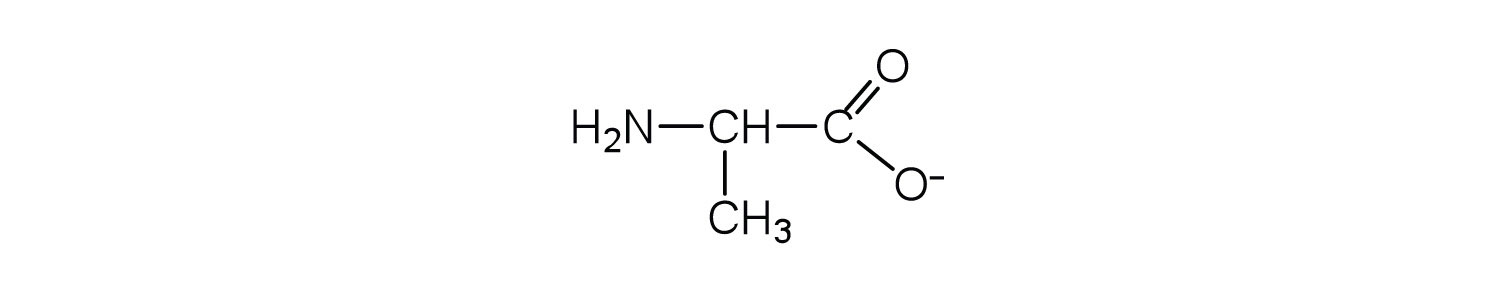
Draw the structure for the anion formed when alanine (at neutral pH) reacts with a base.
-
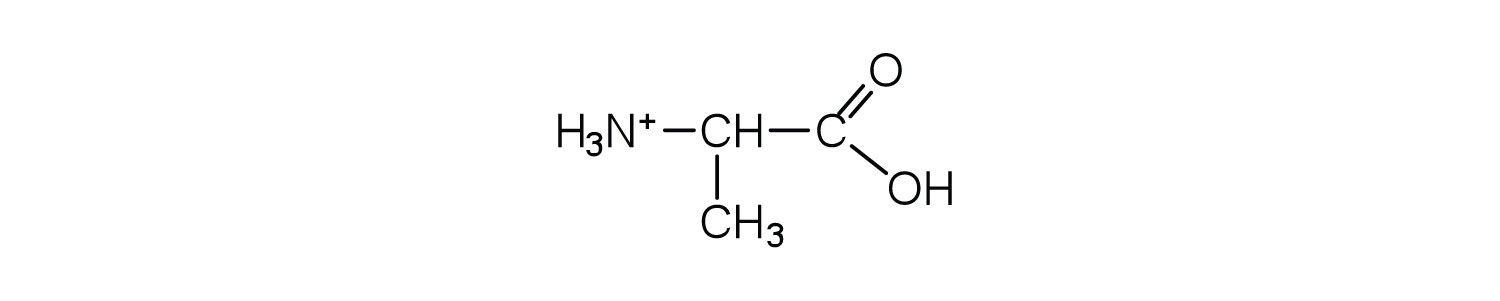
Draw the structure for the cation formed when alanine (at neutral pH) reacts with an acid.
Answers
-
- an electrically neutral compound that contains both negatively and positively charged groups
- the pH at which a given amino acid exists in solution as a zwitterion
-
-
Key Takeaways
- Amino acids can act as both an acid and a base due to the presence of the amino and carboxyl functional groups.
- The pH at which a given amino acid exists in solution as a zwitterion is called the isoelectric point (pI).
Exercises
-
Draw the structure of leucine and determine the charge on the molecule in a(n)
- acidic solution (pH = 1).
- neutral solution (pH = 7).
- a basic solution (pH = 11)
-
Draw the structure of isoleucine and determine the charge on the molecule in a(n)
- acidic solution (pH = 1).
- neutral solution (pH = 7).
- basic solution (pH = 11).