This is “Solving Nonlinear Systems”, section 8.5 from the book Advanced Algebra (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
8.5 Solving Nonlinear Systems
Learning Objectives
- Identify nonlinear systems.
- Solve nonlinear systems using the substitution method.
Nonlinear Systems
A system of equations where at least one equation is not linear is called a nonlinear systemA system of equations where at least one equation is not linear.. In this section we will use the substitution method to solve nonlinear systems. Recall that solutions to a system with two variables are ordered pairs that satisfy both equations.
Example 1
Solve: .
Solution:
In this case we begin by solving for x in the first equation.
Substitute into the second equation and then solve for y.
Here there are two answers for y; use to find the corresponding x-values.
Using |
Using |
|---|---|
This gives us two ordered pair solutions, and
Answer: ,
In the previous example, the given system consisted of a line and a circle. Graphing these equations on the same set of axes, we can see that the two ordered pair solutions correspond to the two points of intersection.
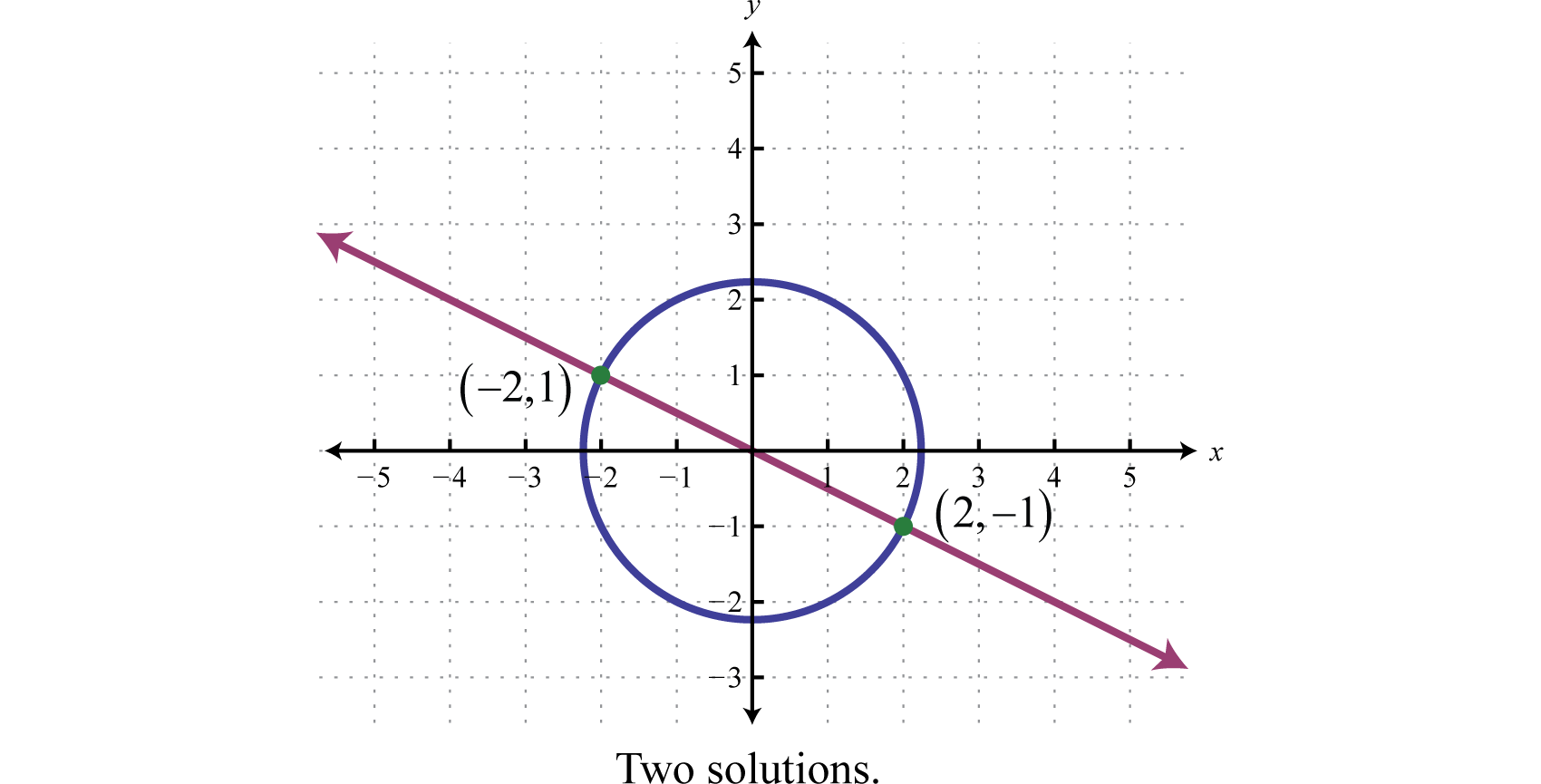
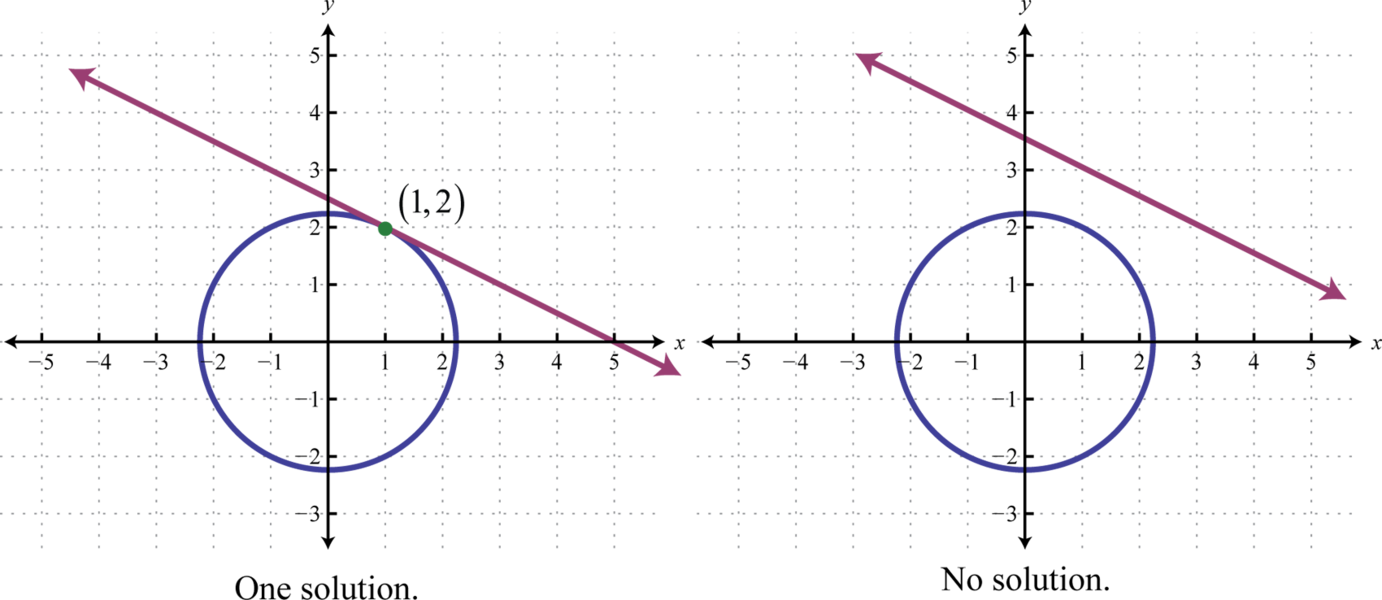
If we are given a system consisting of a circle and a line, then there are 3 possibilities for real solutions—two solutions as pictured above, one solution, or no solution.
Example 2
Solve: .
Solution:
Solve for y in the first equation.
Next, substitute into the second equation and then solve for x.
The resulting equation does not factor. Furthermore, using , , and we can see that the discriminant is negative:
We conclude that there are no real solutions to this equation and thus no solution to the system.
Answer: Ø
If given a circle and a parabola, then there are 5 possibilities for solutions.
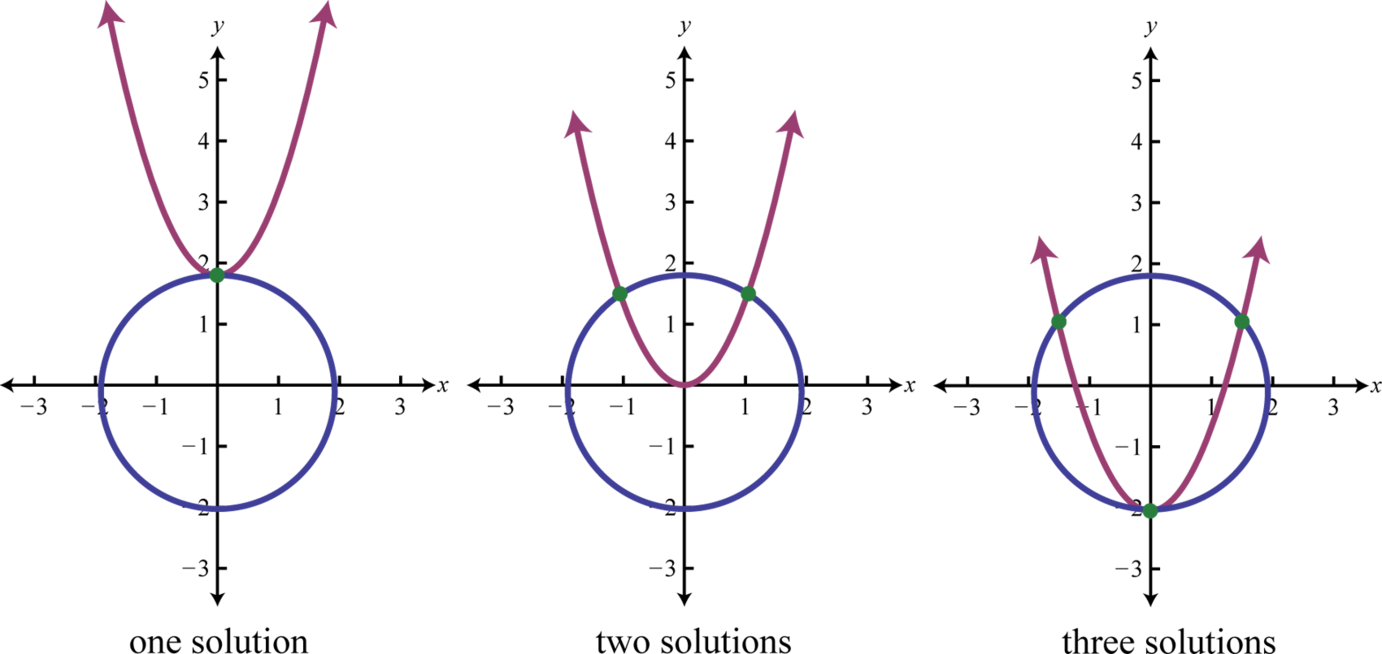
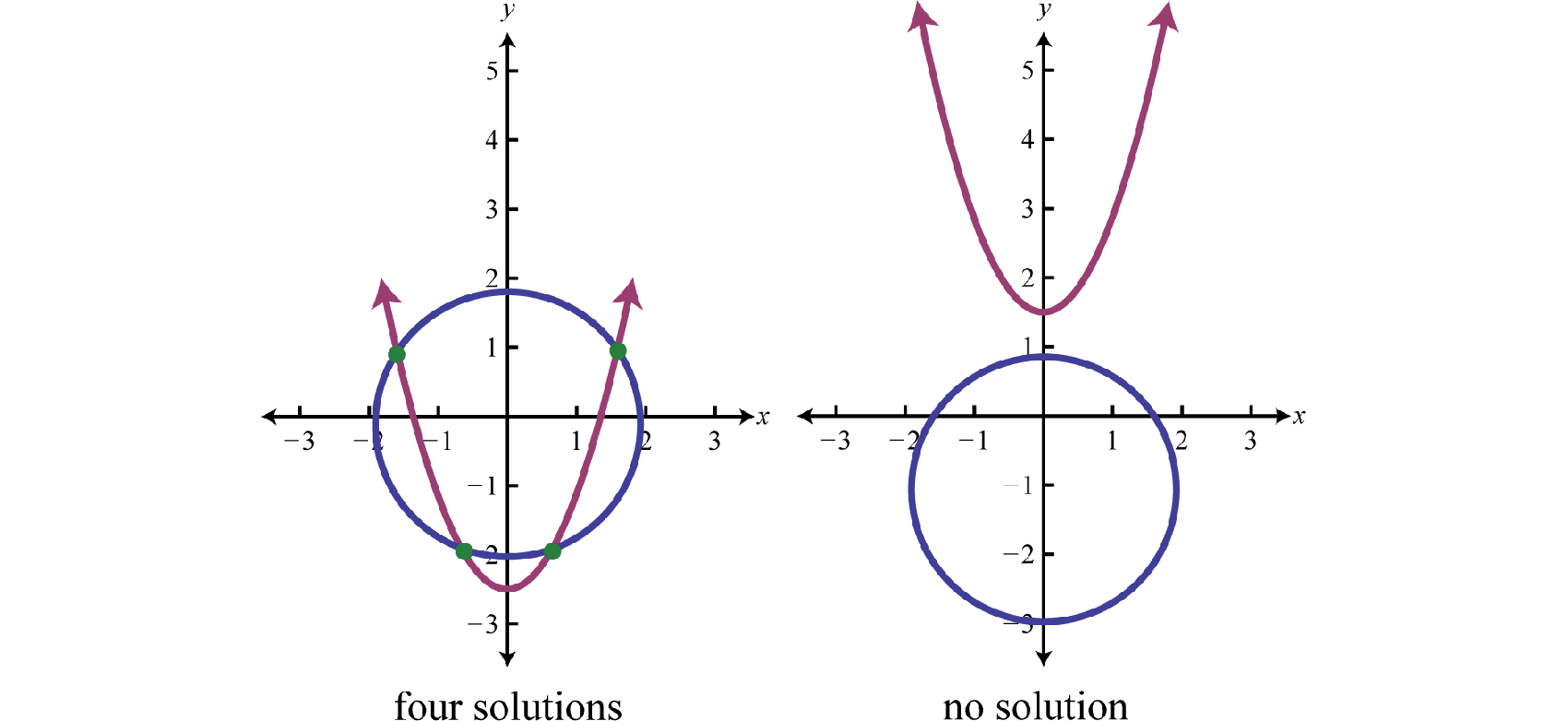
When using the substitution method, we can perform the substitution step using entire algebraic expressions. The goal is to produce a single equation in one variable that can be solved using the techniques learned up to this point in our study of algebra.
Example 3
Solve: .
Solution:
We can solve for in the second equation.
Substitute into the first equation and then solve for y.
Back substitute into to find the corresponding x-values.
Using |
Using |
|---|---|
This leads us to four solutions, and
Answer: ,
Example 4
Solve: .
Solution:
We can solve for in the second equation,
Substitute into the first equation and then solve for x.
Back substitute into to find the corresponding y-values.
Using |
Using |
|---|---|
This leads to three solutions, and
Answer: ,
Example 5
Solve: .
Solution:
Solve for in the second equation.
Substitute into the first equation and then solve for x.
This leaves us with a rational equation. Make a note that and multiply both sides by
At this point we can see that both factors are the same. Apply the zero product property.
Back substitute into to find the corresponding y-values.
Using |
Using |
|---|---|
This leads to two solutions.
Answer: ,
Key Takeaways
- Use the substitution method to solve nonlinear systems.
- Streamline the solving process by using entire algebraic expressions in the substitution step to obtain a single equation with one variable.
- Understanding the geometric interpretation of the system can help in finding real solutions.
Topic Exercises
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The sum of the squares of two positive integers is 10. If the first integer is added to twice the second integer, the sum is 7. Find the integers.
-
The diagonal of a rectangle measures units and has a perimeter equal to 6 units. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
-
For what values of b will the following system have real solutions?
-
For what values of m will the following system have real solutions?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The difference of the squares of two positive integers is 12. The sum of the larger integer and the square of the smaller is equal to 8. Find the integers.
-
The difference between the length and width of a rectangle is 4 units and the diagonal measures 8 units. Find the dimensions of the rectangle. Round off to the nearest tenth.
-
The diagonal of a rectangle measures p units and has a perimeter equal to 2q units. Find the dimensions of the rectangle in terms of p and q.
-
The area of a rectangle is p square units and its perimeter is 2q units. Find the dimensions of the rectangle in terms of p and q.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The diagonal of a rectangle measures units. If the area of the rectangle is 12 square units, find its dimensions.
-
The area of a rectangle is 48 square meters and the perimeter measures 32 meters. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
-
The product of two positive integers is 72 and their sum is 18. Find the integers.
-
The sum of the squares of two positive integers is 52 and their product is 24. Find the integers.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Part A: Nonlinear Systems
Solve.
Solve.
Solve.
Solve.
-
How many real solutions can be obtained from a system that consists of a circle and a hyperbola? Explain.
-
Make up your own nonlinear system, solve it, and provide the answer. Also, provide a graph and discuss the geometric interpretation of the solutions.
Part B: Discussion Board
Answers
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
,
-
-
,
-
-
,
-
-
,
-
-
Ø
-
-
,
-
-
,
-
-
1, 3
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ø
-
-
, ,
-
-
Ø
-
-
, ,
-
-
,
-
-
, , ,
-
-
, , ,
-
-
2, 4
-
-
units by units
-
-
, , ,
-
-
,
-
-
Ø
-
-
-
-
-
-
2 units by 6 units
-
-
6, 12
-
-
-
-
-
-
,
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Answer may vary
-




