This is “Holder in Due Course”, section 18.1 from the book The Legal Environment and Business Law: Master of Accountancy Edition (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
18.1 Holder in Due Course
Learning Objectives
- Understand why the concept of holder in due course is important in commercial transactions.
- Know what the requirements are for being a holder in due course.
- Determine whether a payee may be a holder in due course.
- Know what the shelter rule is and why the rule exists.
Overview of the Holder-in-Due-Course Concept
Importance of the Holder-in-Due-Course Concept
A holder is a person in possession of an instrument payable to bearer or to the identified person possessing it. But a holder’s rights are ordinary, as we noted briefly in Chapter 16 "Nature and Form of Commercial Paper". If a person to whom an instrument is negotiated becomes nothing more than a holder, the law of commercial paper would not be very significant, nor would a negotiable instrument be a particularly useful commercial device. A mere holder is simply an assignee, who acquires the assignor’s rights but also his liabilities; an ordinary holder must defend against claims and overcome defenses just as his assignor would. The holder in due course is really the crux of the concept of commercial paper and the key to its success and importance. What the holder in due course gets is an instrument free of claims or defenses by previous possessors. A holder with such a preferred position can then treat the instrument almost as money, free from the worry that someone might show up and prove it defective.
Requirements for Being a Holder in Due Course
Under Section 3-302 of the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), to be a holder in due course (HDC), a transferee must fulfill the following:
1. Be a holder of a negotiable instrument;
2. Have taken it:
a) for value,
b) in good faith,
c) without notice
(1) that it is overdue or
(2) has been dishonored (not paid), or
(3) is subject to a valid claim or defense by any party, or
(4) that there is an uncured default with respect to payment of another instrument issued as part of the same series, or
(5) that it contains an unauthorized signature or has been altered, and
3. Have no reason to question its authenticity on account of apparent evidence of forgery, alteration, irregularity or incompleteness.
The point is that the HDC should honestly pay for the instrument and not know of anything wrong with it. If that’s her status, she gets paid on it, almost no matter what.
Specific Analysis of Holder-in-Due-Course Requirements
Holder
Again, a holder is a person who possesses a negotiable instrument “payable to bearer or, the case of an instrument payable to an identified person, if the identified person is in possession.”Uniform Commercial Code, Section 1-201(20). An instrument is payable to an identified person if she is the named payee, or if it is indorsed to her. So a holder is one who possesses an instrument and who has all the necessary indorsements.
Taken for Value
Section 3-303 of the UCC describes what is meant by transferring an instrument “for value.” In a broad sense, it means the holder has given something for it, which sounds like consideration. But “value” here is not the same as consideration under contract law. Here is the UCC language:
An instrument is issued or transferred for value if any of the following apply:
(1) The instrument is issued or transferred for a promise of performance, to the extent the promise has been performed.
(2) The transferee acquires a security interest or other lien in the instrument other than a lien obtained by judicial proceeding.
(3) The instrument is issued or transferred as payment of, or as security for, an antecedent claim against any person, whether or not the claim is due.
(4) The instrument is issued or transferred in exchange for a negotiable instrument.
(5) The instrument is issued or transferred in exchange for the incurring of an irrevocable obligation to a third party by the person taking the instrument.
1. For a promise, to the extent performed. Suppose A contracts with B: “I’ll buy your car for $5,000.” Under contract law, A has given consideration: the promise is enough. But this executory (not yet performed) promise given by A is not giving “value” to support the HDC status because the promise has not been performed.
Lorna Love sells her car to Paul Purchaser for $5,000, and Purchaser gives her a note in that amount. Love negotiates the note to Rackets, Inc., for a new shipment of tennis rackets to be delivered in thirty days. Rackets never delivers the tennis rackets. Love has a claim for $5,000 against Rackets, which is not an HDC because its promise to deliver is still executory. Assume Paul Purchaser has a defense against Love (a reason why he doesn’t want to pay on the note), perhaps because the car was defective. When Rackets presents the note to Purchaser for payment, he refuses to pay, raising his defense against Love. If Rackets had been an HDC, Purchaser would be obligated to pay on the note regardless of the defense he might have had against Love, the payee. See Carter & Grimsley v. Omni Trading, Inc., Section 18.3 "Cases", regarding value as related to executory contracts.
A taker for value can be a partial HDC if the consideration was only partly performed. Suppose the tennis rackets were to come in two lots, each worth $2,500, and Rackets only delivered one lot. Rackets would be an HDC only to the extent of $2,500, and the debtor—Paul Purchaser—could refuse to pay $2,500 of the promised sum.
The UCC presents two exceptions to the rule that an executory promise is not value. Section 3-303(a)(4) provides that an instrument is issued or transferred for value if the issuer or transferor gives it in exchange for a negotiable instrument, and Section 3-303(5) says an instrument is transferred for value if the issuer gives it in exchange for an irrevocable obligation to a third party.
2. Security interest. Value is not limited to cash or the fulfillment of a contractual obligation. A holder who acquires a lien on, or a security interest in, an instrument other than by legal process has taken for value.
3. Antecedent debt. Likewise, taking an instrument in payment of, or as security for, a prior claim, whether or not the claim is due, is a taking for value. Blackstone owes Webster $1,000, due in thirty days. Blackstone unexpectedly receives a refund check for $1,000 from the Internal Revenue Service and indorses it to Webster. Webster is an HDC though he gave value in the past.
The rationale for the rule of value is that if the holder has not yet given anything of value in exchange for the instrument, he still has an effective remedy should the instrument prove defective: he can rescind the transaction, given the transferor’s breach of warranty.
In Good Faith
Section 3-103(4) of the UCC defines good faithDefined in the Uniform Commercial Code as “honesty in fact and the observance of reasonable commercial standards of fair dealing.” as “honesty in fact and the observance of reasonable commercial standards of fair dealing.”
Honesty in Fact
“Honesty in fact” is subjectively tested. Suppose Lorna Love had given Rackets, Inc., a promissory note for the tennis rackets. Knowing that it intended to deliver defective tennis rackets and that Love is likely to protest as soon as the shipment arrives, Rackets offers a deep discount on the note to its fleet mechanic: instead of the $1,000 face value of the note, Rackets will give it to him in payment of an outstanding bill of $400. The mechanic, being naive in commercial dealings, has no suspicion from the large discount that Rackets might be committing fraud. He has acted in good faith under the UCC test. That is not to say that no set of circumstances will ever exist to warrant a finding that there was a lack of good faith.
Observance of Reasonable Commercial Standards of Fair Dealing
Whether reasonable commercial standards were observed in the dealings is objectively tested, but buying an instrument at a discount—as was done in the tennis rackets example—is not commercially unreasonable, necessarily.
Without Notice
It obviously would be unjust to permit a holder to enforce an instrument that he knew—when he acquired it—was defective, was subject to claims or defenses, or had been dishonored. A purchaser with knowledge cannot become an HDC. But proving knowledge is difficult, so the UCC at Section 3-302(2) lists several types of notice that presumptively defeat any entitlement to status as HDC. Notice is not limited to receipt of an explicit statement; it includes an inference that a person should have made from the circumstances. The explicit things that give a person notice include those that follow.
Without Notice That an Instrument Is Overdue
The UCC provides generally that a person who has notice that an instrument is overdue cannot be an HDC. What constitutes notice? When an inspection of the instrument itself would show that it was due before the purchaser acquired it, notice is presumed. A transferee to whom a promissory note due April 23 is negotiated on April 24 has notice that it was overdue and consequently is not an HDC. Not all paper contains a due date for the entire amount, and demand paper has no due date at all. In Sections 3-302(a)(2) and 3-304, the UCC sets out specific rules dictating what is overdue paper.
Without Notice That an Instrument Has Been Dishonored
DishonorFailure to pay or refusal to accept a note, a bill, or another commercial obligation. means that instrument is not paid when it is presented to the party who should pay it.
Without Notice of a Defense or Claim
A purchaser of an instrument cannot be an HDC if he has notice that there are any defenses or claims against it. A defense is a reason why the would-be obligor will not pay; a claim is an assertion of ownership in the instrument. If a person is fraudulently induced to issue or make an instrument, he has a claim to its ownership and a defense against paying.
Without Notice of Unauthorized Signature or Alteration
This is pretty clear: a person will fail to achieve the HDC status if he has notice of alteration or an unauthorized signature.
Without Reason to Question the Instrument’s Authenticity Because of Apparent Forgery, Alteration, or Other Irregularity or Incompleteness as to Call into Question Its Authenticity
This also is pretty straightforward, though it is worth observing that a holder will flunk the HDC test if she has notice of unauthorized signature or alteration, or if she should have notice on account of apparent irregularity. So a clever forgery would not by itself defeat the HDC status, unless the holder had notice of it.
Payee as Holder in Due Course
The payee can be an HDC, but in the usual circumstances, a payee would have knowledge of claims or defenses because the payee would be one of the original parties to the instrument. Nevertheless, a payee may be an HDC if all the prerequisites are met. For instance, Blackstone fraudulently convinces Whitestone into signing a note as a comaker, with Greenstone as the payee. Without authority, Blackstone then delivers the note for value to Greenstone. Having taken the note in good faith, for value, without notice of any problems, and without cause to question its validity because of apparent irregularities, Greenstone is an HDC. In any event, typically the HDC is not the payee of the instrument, but rather, is an immediate or remote transferee of the payee.
The Shelter Rule
There is one last point to mention before we get to the real nub of the holder-in-due-course concept (that the sins of her predecessors are washed away for an HDC). The shelter ruleUnder Article 3 of the Uniform Commercial Code, the transferee of an instrument acquires the same rights his or her transferor had. provides that the transferee of an instrument acquires the same rights that the transferor had. Thus a person who does not himself qualify as an HDC can still acquire that status if some previous holder (someone “upstream”) was an HDC.
On June 1, Clifford sells Harold the original manuscript of Benjamin Franklin’s autobiography. Unknown to Harold, however, the manuscript is a forgery. Harold signs a promissory note payable to Clifford for $250,000 on August 1. Clifford negotiates the note to Betsy on July 1 for $200,000; she is unaware of the fraud. On August 2, Betsy gives the note to Al as a token of her affection. Al is Clifford’s friend and knows about the scam (see Figure 18.1 "The Shelter Rule"). May Al collect?
Figure 18.1 The Shelter Rule
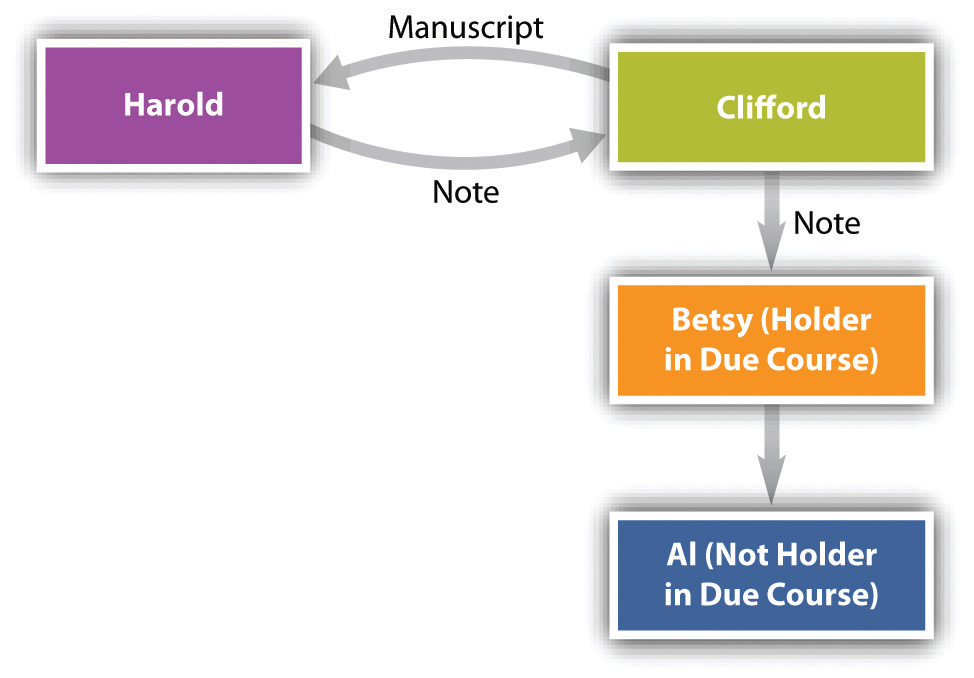
Begin the analysis by noting that Al is not an HDC. Why? For three reasons: he did not take the instrument for value (it was a gift), he did not take in good faith (he knew of the fraud), and he had notice (he acquired it after the due date). Nevertheless, Al is entitled to collect from Harold the full $250,000. His right to do so flows from UCC, Section 3-203(b): “Transfer of an instrument, whether or not the transfer is a negotiation, vests in the transferee any right of the transferor to enforce the instrument, including any right as a holder in due course, but the transferee cannot acquire rights of a holder in due course by a direct or indirect transfer from a holder in due course if the transferee engaged in fraud or illegality affecting the instrument.”
By virtue of the shelter rule, Al as transferee from Betsy acquires all rights that she had as transferor. Clearly Betsy is an HDC: she paid for the instrument, she took it in good faith, had no notice of any claim or defense against the instrument, and there were no apparent irregularities. Since Betsy is an HDC, so is Al. His knowledge of the fraud does not undercut his rights as HDC because he was not a party to it and was not a prior holder. Now suppose that after negotiating the instrument to Betsy, Clifford repurchased it from her. He would not be an HDC—and would not acquire all Betsy’s rights—because he had been a party to fraud and as a prior holder had notice of a defense. The purpose of the shelter rule is “to assure the holder in due course a free market for the paper.”Uniform Commercial Code, Section 3-203, Comment 2.
Key Takeaway
The holder-in-due-course doctrine is important because it allows the holder of a negotiable instrument to take the paper free from most claims and defenses against it. Without the doctrine, such a holder would be a mere transferee. The UCC provides that to be an HDC, a person must be a holder of paper that is not suspiciously irregular, and she must take it in good faith, for value, and without notice of anything that a reasonable person would recognize as tainting the instrument. A payee may be an HDC but usually would not be (because he would know of problems with it). The shelter rule says that a transferee of an instrument acquires the same rights her transferor had, so a person can have the rights of an HDC without satisfying the requirements of an HDC (provided she does not engage in any fraud or illegality related to the transaction).
Exercises
- Summarize the requirements to be a holder in due course.
- Why is the status of holder in due course important in commercial transactions?
- Why is it unlikely that a payee would be a holder in due course?
- What is the shelter rule, and why does it exist?




