This is “Mobile Phones: More than Phone Calls”, section 16.3 from the book Online Marketing Essentials (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
16.3 Mobile Phones: More than Phone Calls
Learning Objective
- Learn about the three categories of mobile phones and how they fit into the eMarketing landscape.
There are three categories of mobile phones.
Basic phonesThese are standard handsets that can make and receive voice calls, send and receive text messages, and make use of USSD services. can make voice calls, send and receive SMS (short message service) messages and make use of USSD (unstructured supplementary services data)Works on all existing GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) phones. Provides session-based communication, enabling a variety of applications..
Feature phonesThese are handsets that offer additional functionality and often include a camera and additional storage space. Often they can access the Internet, but they generally have a standard numeric keypad. offer features additional to a basic phone, including cameras and increased storage, as well as the ability to access the Internet. Feature phones usually have a standard numeric keypad.
Note
QWERTY refers to a full keypad like the keyboard of a computer.
SmartphonesHandsets with advanced capabilities that allow users to add applications to their phones. They usually have a QWERTY keypad and include 3G and Wi-Fi capabilities. offer advanced capabilities and features over feature phones, notably allowing users to add applications to their phones. These phones run a full-featured operating system; most have 3GThird generation of mobile communications systems. 3G networks enable network operators to offer users a wider range of more advanced services while achieving greater network capacity. (third-generation) as well as Wi-FiAny of a family of wireless local area network (LAN) data standards (IEEE 802.11) used fairly ubiquitously for corporate and home connectivity. Also available as hotspots in public areas such as cafes and airport terminals, either for free or for a one-time-use charge or subscription fee. (wireless-fidelity) capabilities and generally have a QWERTY keypad.
Note that there is not yet an industry-standard definition of a smartphone, and many feature phones are now being developed with technology similar to smartphones. Smartphones tend to have bigger screens than feature phones.
Figure 16.1 Features of a Mobile Phone
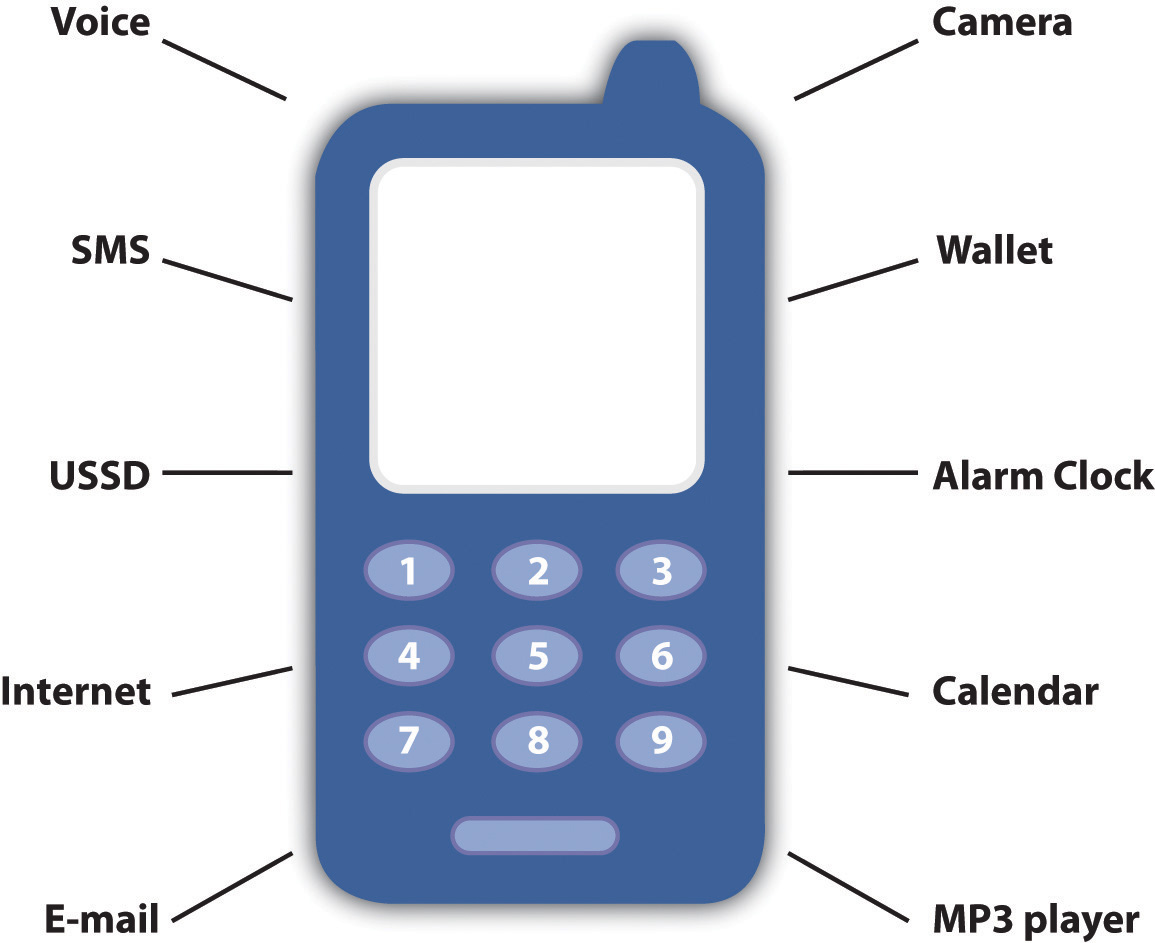
How to Reach Your Audience
Just as the Web is used in a myriad of ways as a marketing, advertising, and distribution channel, so is the mobile phone. There are a number of technologies available to reach a mobile audience. Some of the most prevalent are detailed further.
Mobile phones started as literally phones that are mobile (thank you again, Captain Obvious). Before we look at mobile phones as devices used to access the World Wide Web, to take photographs, or to make payments, we need to address their primary function: communication. The primary use of a mobile phone is to enable communication, either through voice calls or through messages. Messaging services on a mobile phone use either short message service (SMS) to send text messages or multimedia message service (MMS)An extension on SMS (short message service); allows picture, sound, or low-quality videos to be sent on a wireless network. to send graphics, audio, photos, and video as well as text. Messages can, of course, also be sent via e-mail depending on the phone’s features.
Note
Do u find it tricky to transl8 txt msgs? http://www.transl8it.com translates from text speak into everyday English and back again.
Key Takeaways
- There are three categories of mobile phones: basic phones, feature phones, and smartphones.
- Smartphones are equipped with a QWERTY keypad.
- The mobile phone is primarily a communication device that uses voice, SMS, or MMS.
Exercises
- Consider the three categories of mobile phone. Envision the advertising opportunities available on each.
- What types of mobile phones have you ever used? Have you been marketed to before on these phone(s)? If so, how?




