This is “How It Works”, section 7.2 from the book Online Marketing Essentials (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
7.2 How It Works
Learning Objectives
- Understand how PPC (pay per click) works.
- Learn what makes up a PPC advertisement.
Each of the three major search engines (Google, Yahoo! and MSN Bing) has its own pay-per-click (PPC) advertisingBidding for sponsored advertisements on search engine results pages and paying only when the advertisement is clicked on. platform, namely, AdWordsGoogle’s PPC (pay-per-click) advertising system., Yahoo! Search MarketingYahoo!’s PPC (pay-per-click) advertising, powered by the Panama platform., and adCenterMicrosoft’s PPC (pay-per-click) advertising system.. While the basic process remains the same for each one, there are some differences.
With PPC advertising, the advertiser does the following:
- Creates the content for an advertisement
- Selects the keywordsThis is a word found within a search query. For example, searching for “blue widgets” includes the keywords “blue” and “widgets.” for which that advertisement should appear
- Chooses the maximum amount they are willing to pay for a click on the advertisement (this amount can be unique to each keyword they have selected for an advertisement)
The search engine algorithm does the following:
- Checks the advertisement for compliance to editorial guidelines
- Displays the advertisement for relevant search queries
- Determines the rank, or position, of the advertisement based on the advertiser’s maximum bid and the relevance of the advertisement (which includes factors such as click-through rate [CTR], ad copy, keywords, and landing-page relevance to the search)
Search and Content Networks
Advertisers can choose to have their advertisements displayed on the search network only (which means on search engines), or they can select to have the advertisements displayed on the content network.
The search network will include the search engine that owns the platform (so Google for AdWords), as well as other search engines for which that platform provides paid results (e.g., currently Ask.com uses the AdWords platform for paid results).
Figure 7.2 Suppliers and Search Engines as of 2007“Search Engine Results Chart,” Search Engine Watch, March 23, 2007, http://searchenginewatch.com/2167981 (accessed June 18, 2010).
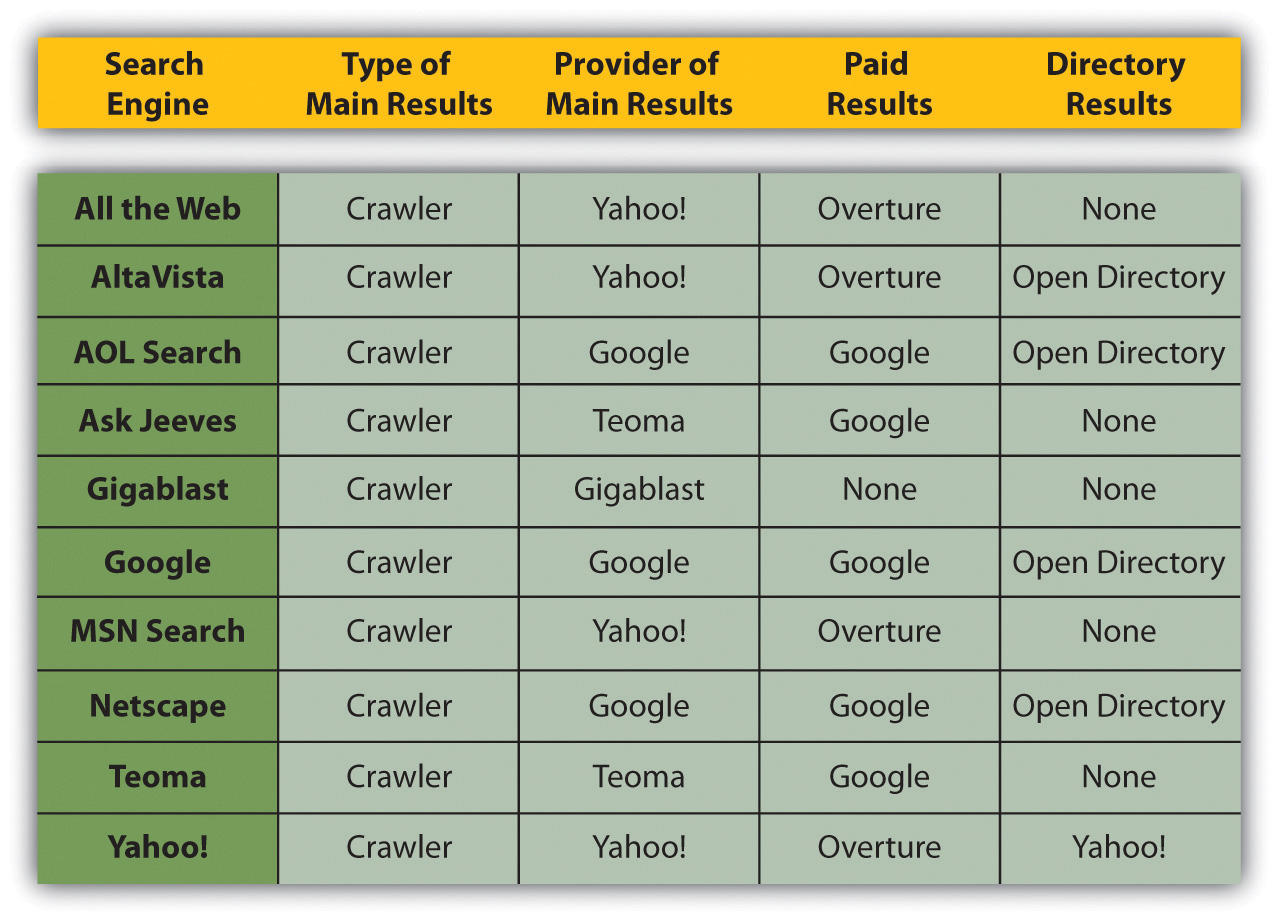
The content network refers to Web sites other than search engines that also display PPC advertisements. For Google AdWords, these are the Web sites and blogs that have joined Google AdSense, Google’s publishers’ platform. Google determines the content of the Web site and then displays appropriate PPC advertisements. Typically, the CPC (cost per click)Paid when a link is clicked upon. for text ads is lower than on the search network, but the CTR and conversion ratePercentage of actions divided by click. can be much lower. The Google content network also allows image, video, and mobile ads.
Figure 7.3
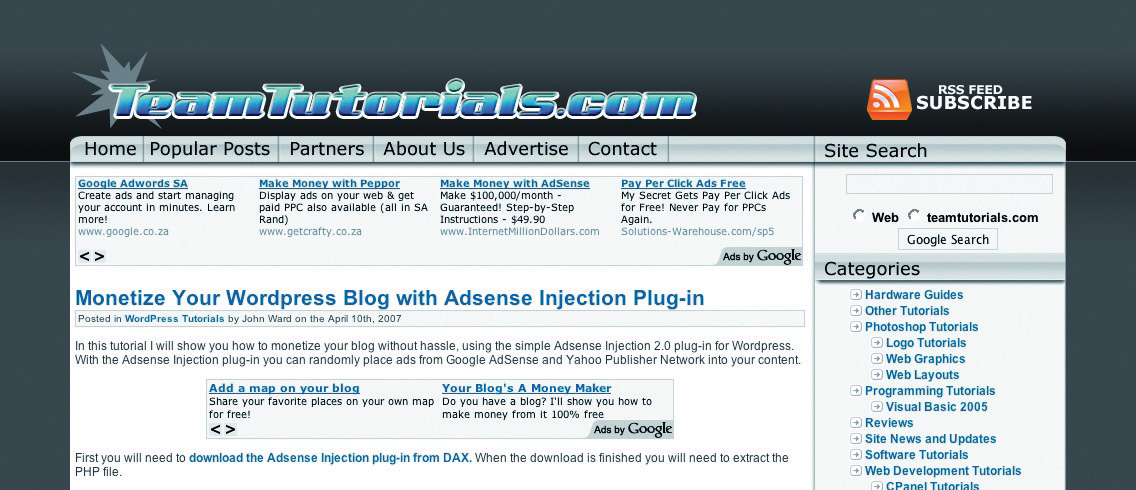
The site below is running AdSense. Notice how the advertisements correlate to the content of the article.
Discussion
Why do you think the CTR and conversion rate are lower on content PPC advertisements as opposed to search PPC advertisements?
What Makes Up a PPC Advertisement?
Text PPC advertisements follow the same basic structure:
Heading
Two lines of advertisement copy,
Which can be displayed on one line
www.DisplayURL.com
The URL (uniform resource locator) shown is not necessarily the URL that the user will click through to. When writing the copy, these are known as the display URL (what is shown on the advertisement) and the destination URL (what the actual URL of the page is). The display URL is sometimes also called a vanity URL. The aim should be to send users to a Web page as specific to their search, and the PPC advertisement, as possible. This is known as deep linkingMaking a hyperlink that points to a specific page or image on another Web site instead of that Web site’s main or home page..
Discussion
What is the function of the display URL? Do you think that this is misleading to a searcher? Why do you think the display and the destination URL are different?
The display URL must be the same domain as the destination URL. Google will only show one advertisement per display URL. So an advertisement might look like this:
Roses for Valentine’s
A dozen red roses for your love;
Fast, free delivery in RSA.
www.flowers.co.za/roses
The search engines limit the characters in each line. There are also restrictions on what you are allowed to write in an advertisement. Here are some of the editorial guidelines from Google AdWords:
- Heading. Maximum twenty-five characters
- Line 1. Maximum thirty-five characters
- Line 2. Maximum thirty-five characters
- Display URL. Maximum thirty-five characters
- No repeated exclamation marks
- No word may be written in capitals only
- No nonsense words may be used
- No claims of “best,” “number one,” or superlatives may be used unless they can be verified by a reliable third-party source
- Product numbers may be used
Key Takeaways
- In PPC (pay per click), an advertiser develops the content for an ad, selects keywords for the ad, and chooses the maximum amount they are willing to pay for a click.
- A search algorithm checks the ad for compliance with editorial guidelines, displays the ad for relevant search queries, determines the rank of the ad based on the max bid, and determines the relevance of the ad.
- Search engines have specific guidelines for advertisements.
Exercises
- What is the difference between the display URL and the landing page URL, and what is the function of each?
- How is the content network different from the search network? How do the differences affect the advertiser?




