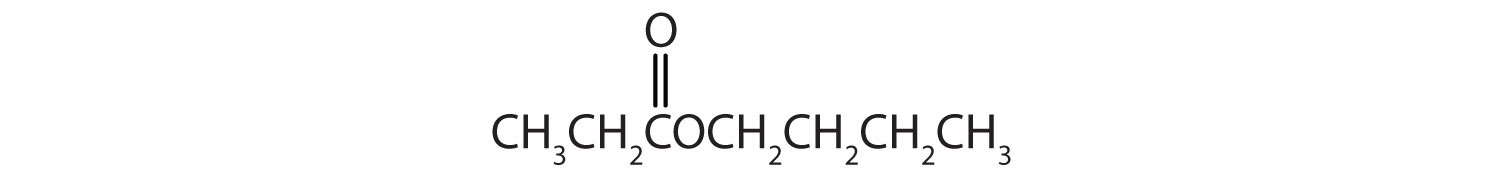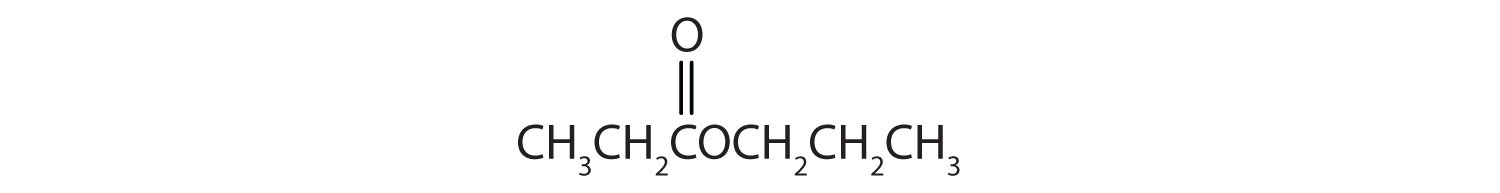This is “Esters: Structures and Names”, section 15.6 from the book Introduction to Chemistry: General, Organic, and Biological (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
15.6 Esters: Structures and Names
Learning Objectives
- Identify the general structure for an ester.
- Use common names to name esters.
- Name esters according to the IUPAC system.
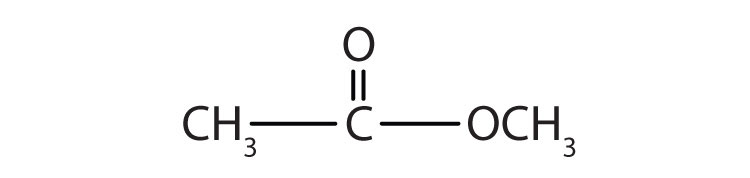
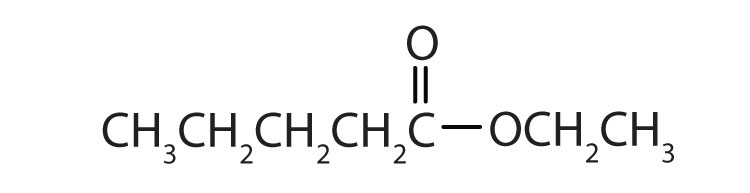
Esters have the general formula RCOOR′, where R may be a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, or an aryl group, and R′ may be an alkyl group or an aryl group but not a hydrogen atom. (If it were hydrogen atom, the compound would be a carboxylic acid.) Figure 15.4 "The Structure of Esters" shows models for two common esters.
Figure 15.4 The Structure of Esters
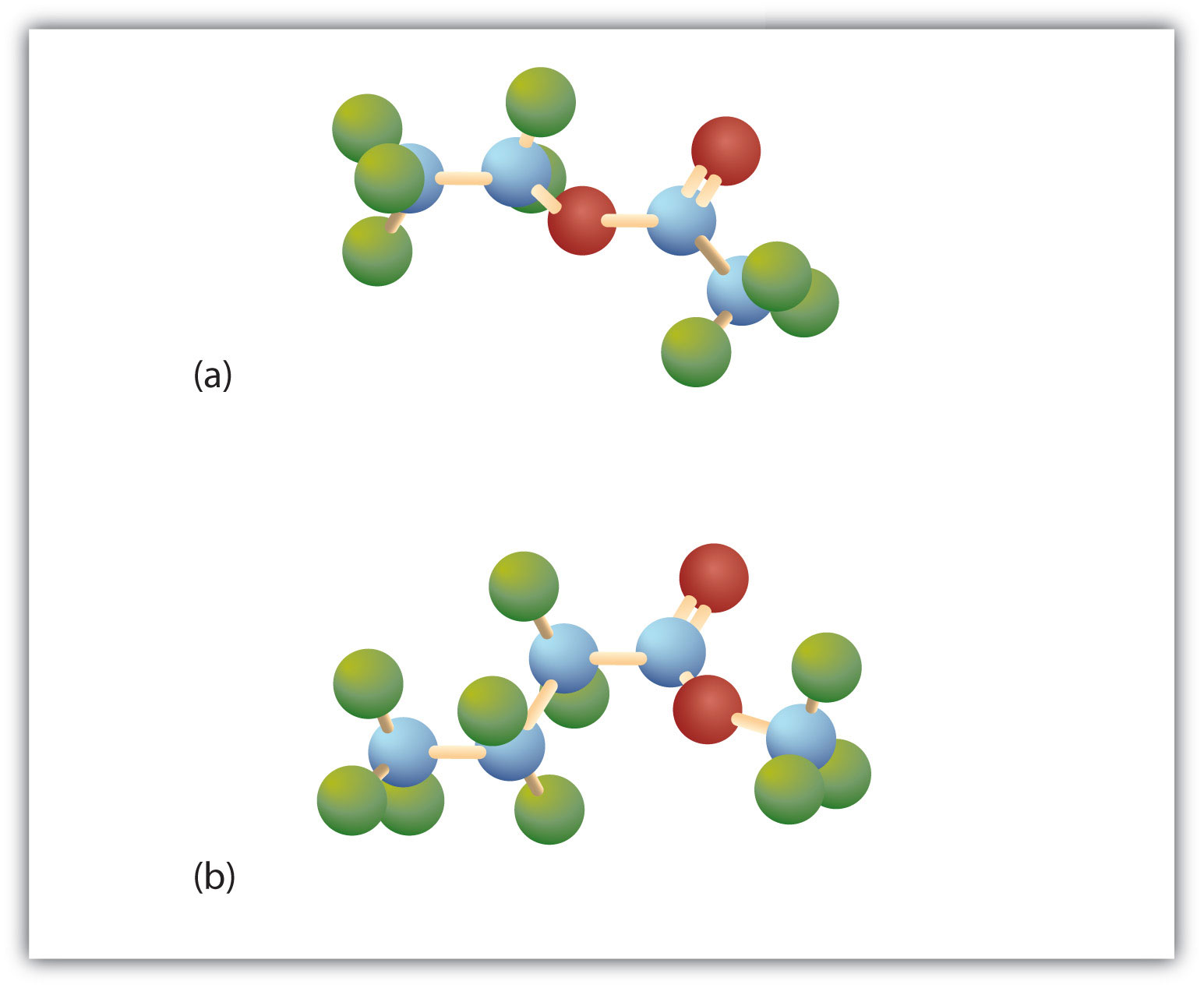
Esters feature a carbon-to-oxygen double bond that is also singly bonded to a second oxygen atom, which is then joined to an alkyl or an aryl group. The esters shown here are ethyl acetate (a) and methyl butyrate (b).
Esters occur widely in nature. Unlike carboxylic acids, esters generally have pleasant odors and are often responsible for the characteristic fragrances of fruits and flowers. Once a flower or fruit has been chemically analyzed, flavor chemists can attempt to duplicate the natural odor or taste. Both natural and synthetic esters are used in perfumes and as flavoring agents.
Note
Fats and vegetable oils are esters of long-chain fatty acids and glycerol. Esters of phosphoric acid are of the utmost importance to life. (For more information about fats/oils and esters, see Chapter 17 "Lipids", Section 17.2 "Fats and Oils", and Section 15.10 "Esters of Phosphoric Acid", respectively.)
Names of Esters
Although esters are covalent compounds and salts are ionic, esters are named in a manner similar to that used for naming salts. The group name of the alkyl or aryl portion is given first and is followed by the name of the acid portion. In both common and International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature, the -ic ending of the parent acid is replaced by the suffix -ate (Table 15.3 "Nomenclature of Esters").
Table 15.3 Nomenclature of Esters
| Condensed Structural Formula | Common Name | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|---|
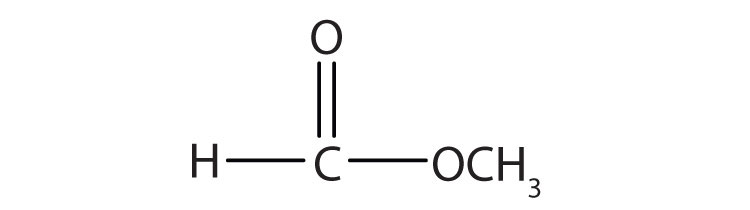
| HCOOCH3 | methyl formate | methyl methanoate |
| CH3COOCH3 | methyl acetate | methyl ethanoate |
| CH3COOCH2CH3 | ethyl acetate | ethyl ethanoate |
| CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 | ethyl propionate | ethyl propanoate |
| CH3CH2CH2COOCH(CH3)2 | isopropyl butyrate | isopropyl butanoate |
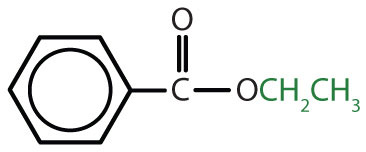
|
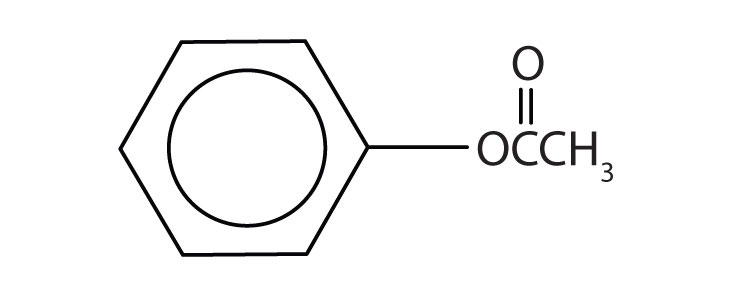
ethyl benzoate | ethyl benzoate |
Example 5
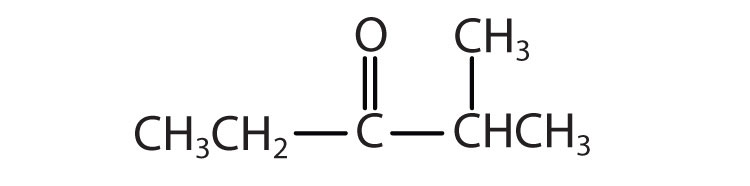
Give the common and IUPAC names for each compound.
Solution
-
The alkyl group attached directly to the oxygen atom is a butyl group (in green).
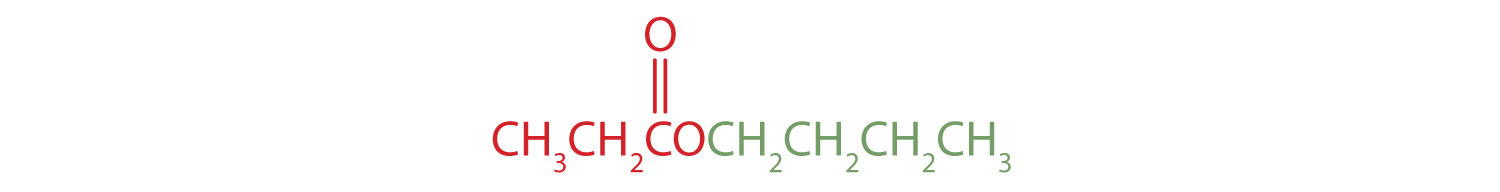
The part of the molecule derived from the carboxylic acid (in red) has three carbon atoms. It is called propionate (common) or propanoate (IUPAC). The ester is therefore butyl propionate or butyl propanoate.
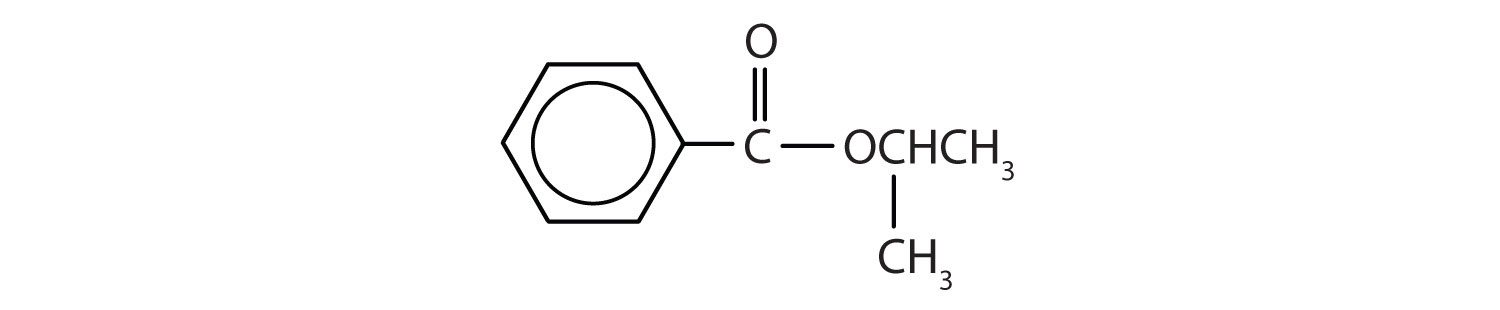
-
An alkyl group (in green) is attached directly to the oxygen atom by its middle carbon atom; it is an isopropyl group. The part derived from the acid (that is, the benzene ring and the carbonyl group, in red) is benzoate. The ester is therefore isopropyl benzoate (both the common name and the IUPAC name).
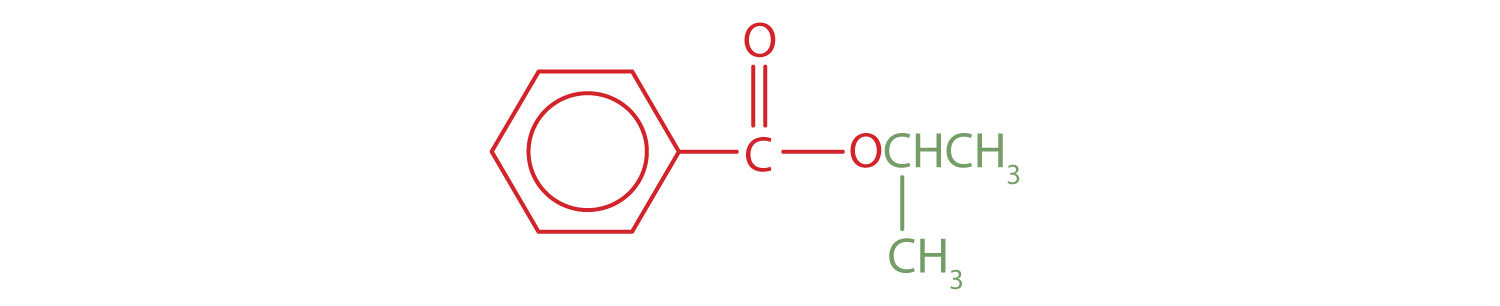
Skill-Building Exercise
Give the common and IUPAC names for each compound.
Example 6
Draw the structure for ethyl pentanoate.
Solution
Start with the portion from the acid. Draw the pentanoate (five carbon atoms) group first; keeping in mind that the last carbon atom is a part of the carboxyl group.
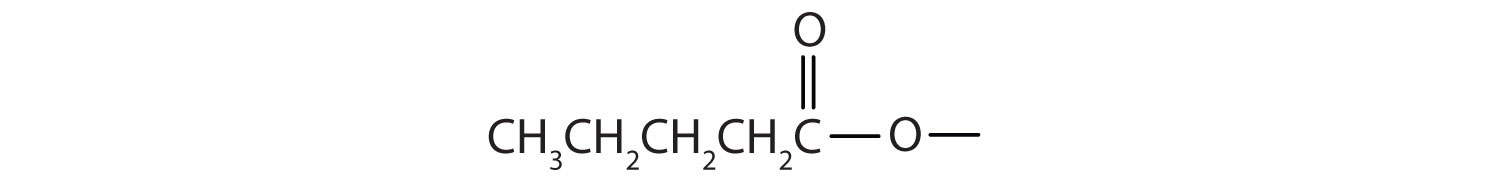
Then attach the ethyl group to the bond that ordinarily holds the hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group.
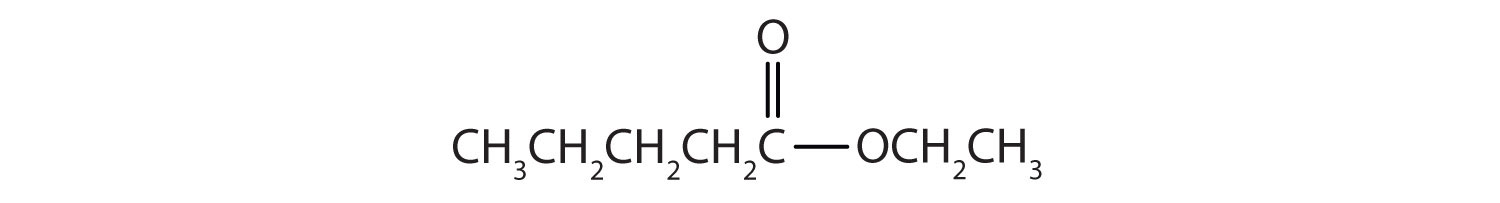
Skill-Building Exercise
-
Draw the structure for phenyl pentanoate.
Concept Review Exercises
-
From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can isopropyl hexanoate be made?
-
From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can cyclobutyl butyrate be made?
Answers
-
hexanoic acid and isopropyl alcohol
-
butyric acid and cyclobutyl alcohol
Key Takeaway
- An ester has an OR group attached to the carbon atom of a carbonyl group.
Exercises
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- methyl acetate
- ethyl pentanoate
- phenyl acetate
- isopropyl propionate
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- ethyl hexanoate
- ethyl benzoate
- phenyl benzoate
- ethyl 3-methylhexanoate
-
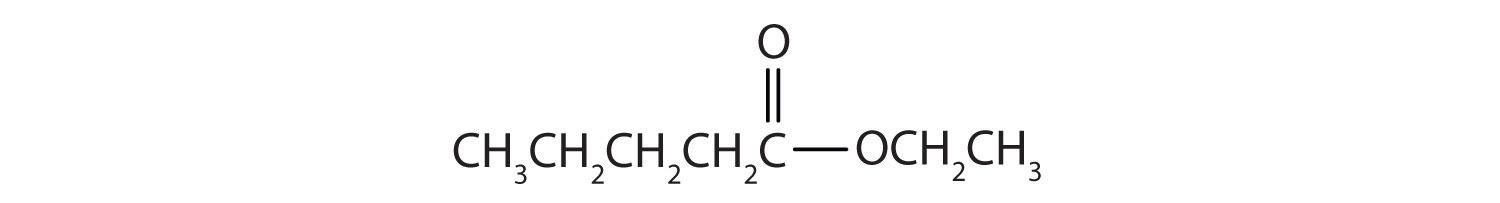
Name each compound with both the common name and the IUPAC name.
-
-
Name each compound with both the common name and the IUPAC name.
-
Answers
-
-
-
-
- methyl formate; methyl methanoate
- ethyl propionate; ethyl propanoate
-