This is “Conclusion”, section 10.7 from the book Creating Services and Products (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
10.7 Conclusion
In this chapter, we have discussed the concept of lock-in and identified various issues on the lock-in such as how companies can achieve it, the downside of it, and the lock-in index for practical use. We also have addressed the relationship between the lock-in and companies’ absorptive capacity within the framework of outsourcing. The key points are the following:
- Lock-in is pervasive. It is part of the normal day-to-day transactions in business.
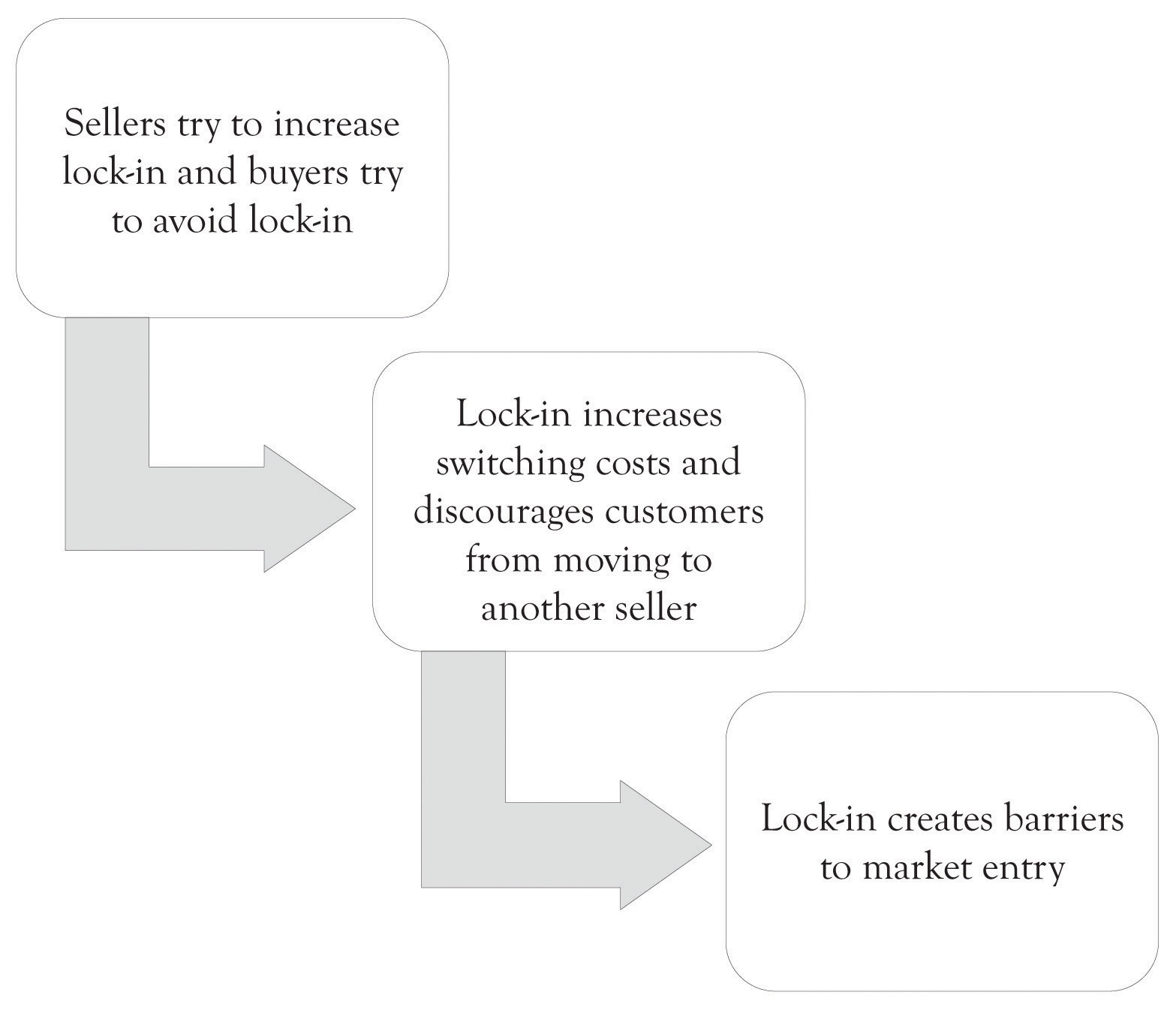
- If you are a producer, then you need to take steps to acquire customers so that you can lock them in (see Figure 10.3 "Lock-In Issues"). This may include giving potential customers money, providing additional complimentary services, and developing attractive incentives for participation.
- Producers will always try to lock-in consumers. It is important that consumers try to get producers to offer incentives in order to offset present and future switching costs.
- The initial stage of bargaining is important because once the consumer has committed to a seller, then the lock-in has been cast. If you are a business and are considering outsourcing, then you will be locked-in as soon as you sign on the dotted line. In that case, you should look for second sources.
- When a company or an individual outsources, they are essentially merging with another entity that has a competitive advantage in a particular area. Identifying the processes where having a core competency is critical for the firm to survive and to engage in learn-by-doing activity in that area.
Figure 10.3 Lock-In Issues