This is “The Role of R&D Process in Innovation”, section 1.13 from the book Creating Services and Products (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
1.13 The Role of R&D Process in Innovation
The objectives of R&D are to develop existing and new core competencies, to further existing and new products, and to develop existing and new business processes through invention and innovation.Matheson and Matheson (1998). The R&D process is the engine that drives product and process differentiation. InnovationThe ideas, products, services, or processes that are perceived as being new and different and that have been implemented or even commercialized. is typically defined as the ideas, the products, the services, or processes that are perceived as being new and different and they have been implemented or even commercialized.
Research and development are usually thrown together as one concept, but in reality they are somewhat distinct processes.Annacchino (2006). ResearchTypically considered to be science-oriented. is typically considered to be science-oriented whereas developmentThe mechanism for translating the science of research into commercial products and services. is the mechanism for translating the science into commercial products and services. Basic science can be thought of as the engine for pushing new discoveries and ideas into society. This is in contrast to the concept of market pull. Market pullThe process of translating the basic science into products and services in order to satisfy customer needs, wants, and demands. is essentially the process of translating the basic science into products and services in order to satisfy customer needs, wants, and demands. The interaction between science push and market pull creates a very powerful feedback loop that spurs on the development and diffusion of new products and services.Schmoch (2007).
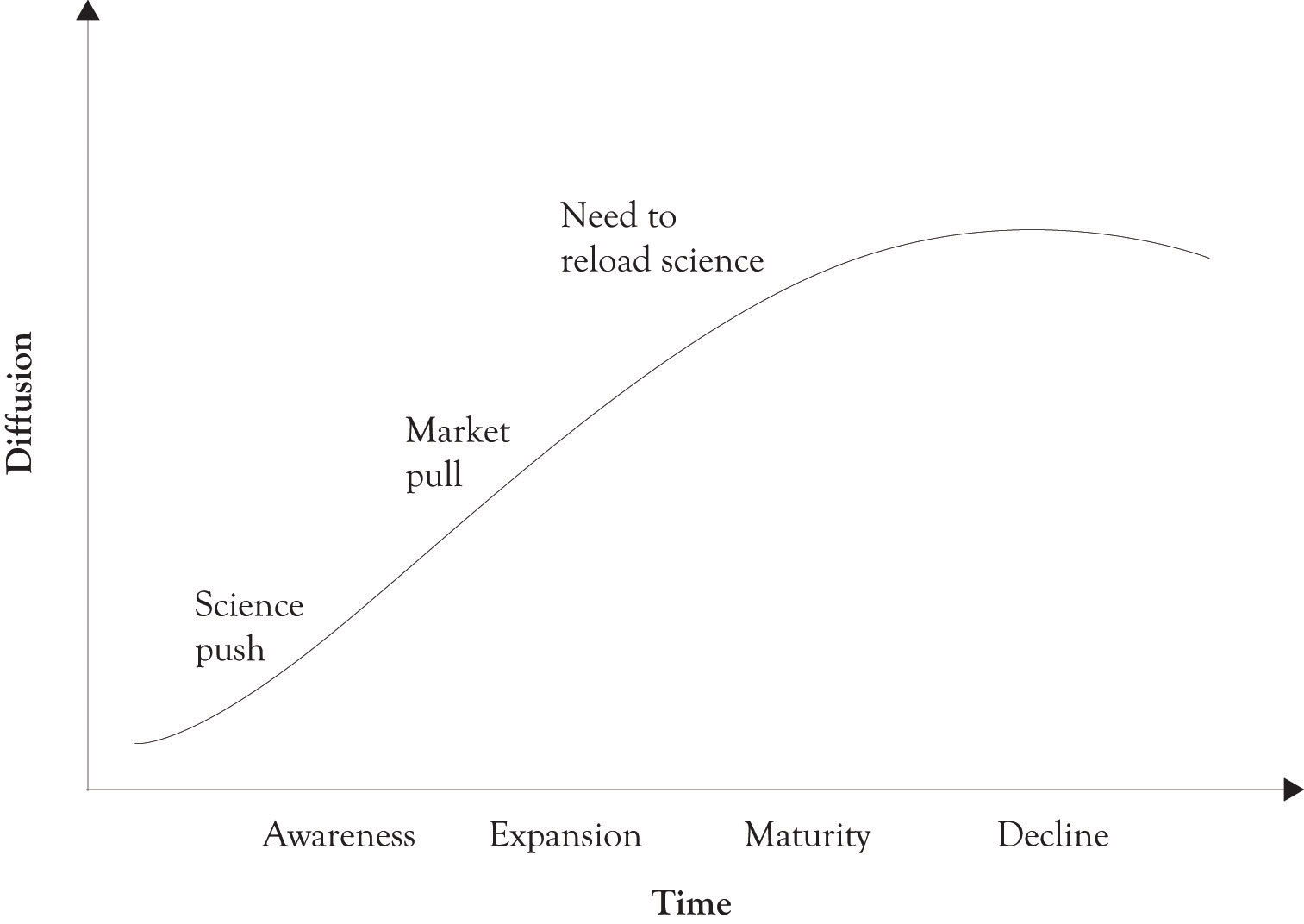
As noted earlier, the diffusion and awareness of technologies typically follows an S-curve. In the early stages of the S-curve, there are very few people aware of the technology. Market research is not important at this stage because there are few untapped wants because of the lack of awareness. As a technology matures and begins to take off, there is a propagation of awareness with increased insight of the possibilities of a technology.Goldenberg and Mazursky (2002). It is at this stage that market research becomes viable. It is also at this stage that many similar products begin to emerge because of the surfacing of a kind of group aha because of the interconnectedness of businesses and research groups. This group aha occurs because market research by producers and product development laboratories leads to the same conclusions about consumer wants. Once consumers begin to use products and have had the opportunity to experience a product, they also begin to identify areas of deficiencies in the product and areas where a feature might be added. And this is where market research is very effective because market researchers are very adept at identifying changes in consumer wants.
As the market matures, the demand for the products also begins to decline with the emergence of substitute products and technological obsolescence. It is then necessary to re-prime the pump and reload science. This is done by working with new science and new technologies in order to identify new opportunities for developing products and services. Figure 1.8 "Push, Pull, and Reload" illustrates the concepts of science push and market pull and how they relate to diffusion and awareness.
Figure 1.8 Push, Pull, and Reload