This is “Perfect Competition and Supply and Demand”, section 1.4 from the book An Introduction to Business (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
1.4 Perfect Competition and Supply and Demand
Learning Objective
- Describe perfect competition, and explain how supply and demand interact to set prices in a free market system.
Under a mixed economy, such as we have in the United States, businesses make decisions about which goods to produce or services to offer and how they are priced. Because there are many businesses making goods or providing services, customers can choose among a wide array of products. The competition for sales among businesses is a vital part of our economic system. Economists have identified four types of competition—perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. We’ll introduce the first of these—perfect competition—in this section and cover the remaining three in the following section.
Perfect Competition
Figure 1.6

Produce, like these apples, is a standardized product available from numerous businesses.
© 2010 Jupiterimages Corporation
Perfect competitionMarket in which many consumers buy standardized products from numerous small businesses. exists when there are many consumers buying a standardized product from numerous small businesses. Because no seller is big enough or influential enough to affect price, sellers and buyers accept the going price. For example, when a commercial fisher brings his fish to the local market, he has little control over the price he gets and must accept the going rate.
The Basics of Supply and Demand
To appreciate how perfect competition works, we need to understand how buyers and sellers interact in a market to set prices. In a market characterized by perfect competition, price is determined through the mechanisms of supply and demand. Prices are influenced both by the supply of products from sellers and by the demand for products by buyers.
To illustrate this concept, let’s create a supply and demand schedule for one particular good sold at one point in time. Then we’ll define demand and create a demand curve, and define supply and create a supply curve. Finally, we’ll see how supply and demand interact to create an equilibrium price—the price at which buyers are willing to purchase the amount that sellers are willing to sell.
Demand and the Demand Curve
DemandQuantity of a product that buyers are willing to purchase at various prices. is the quantity of a product that buyers are willing to purchase at various prices. The quantity of a product that people are willing to buy depends on its price. You’re typically willing to buy less of a product when prices rise and more of a product when prices fall. Generally speaking, we find products more attractive at lower prices, and we buy more at lower prices because our income goes further.
Figure 1.7 The Demand Curve
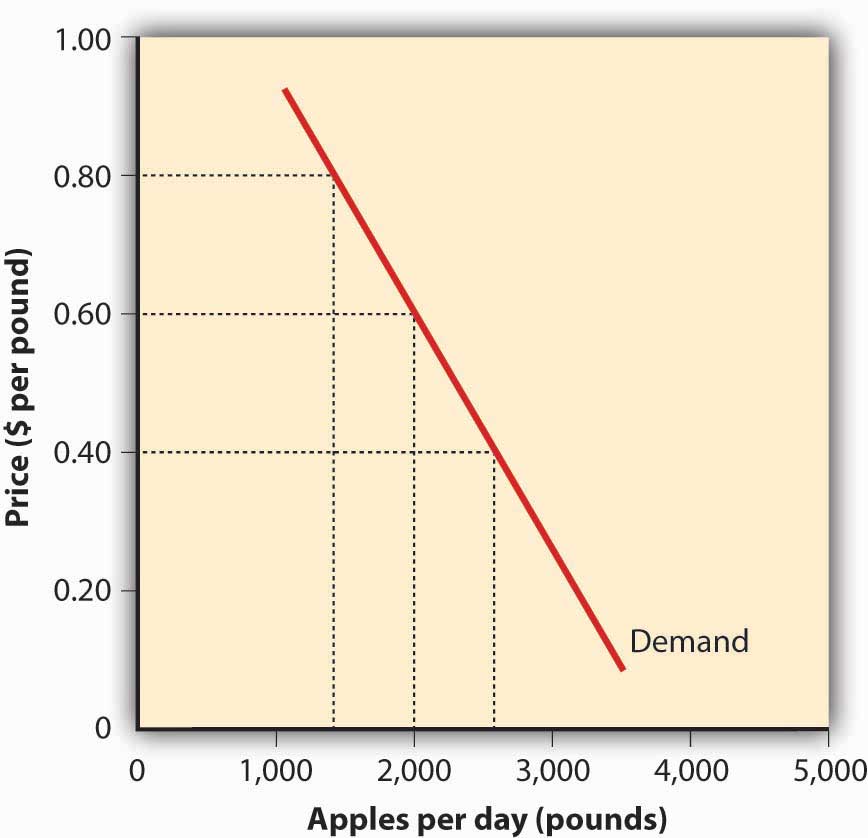
Using this logic, we can construct a demand curveGraph showing the quantity of a product that will be bought at certain prices. that shows the quantity of a product that will be demanded at different prices. Let’s assume that the diagram in Figure 1.7 "The Demand Curve" represents the daily price and quantity of apples sold by farmers at a local market. Note that as the price of apples goes down, buyers’ demand goes up. Thus, if a pound of apples sells for $0.80, buyers will be willing to purchase only fifteen hundred pounds per day. But if apples cost only $0.60 a pound, buyers will be willing to purchase two thousand pounds. At $0.40 a pound, buyers will be willing to purchase twenty-five hundred pounds.
Supply and the Supply Curve
SupplyQuantity of a product that sellers are willing to sell at various prices. is the quantity of a product that sellers are willing to sell at various prices. The quantity of a product that a business is willing to sell depends on its price. Businesses are more willing to sell a product when the price rises and less willing to sell it when prices fall. Again, this fact makes sense: businesses are set up to make profits, and there are larger profits to be made when prices are high.
Figure 1.8 The Supply Curve
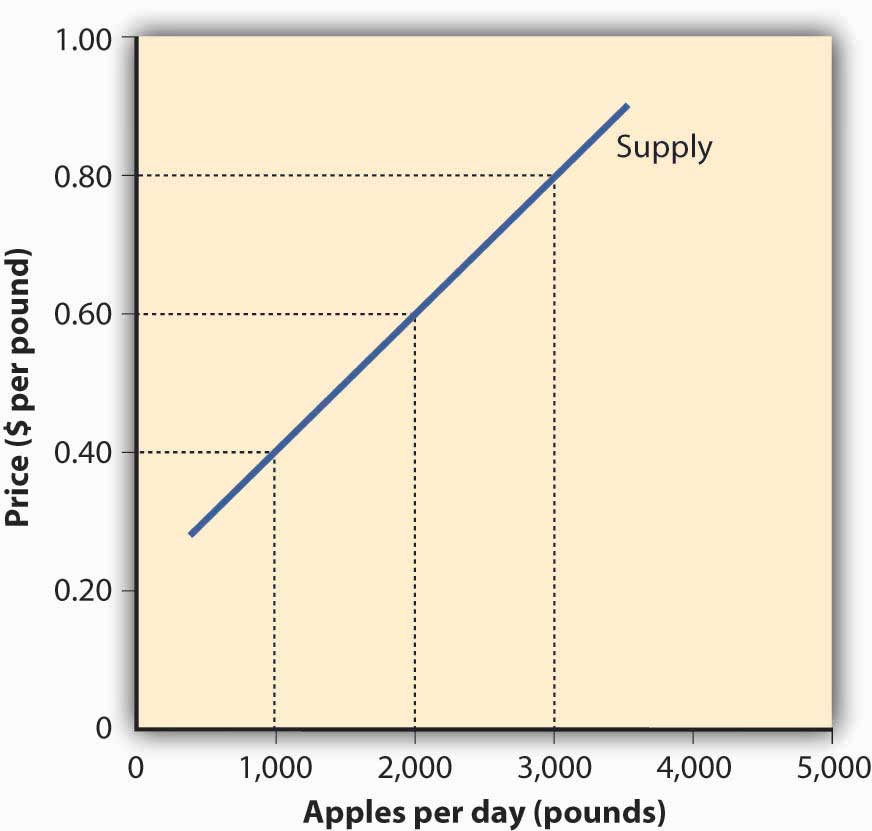
Now we can construct a supply curveGraph showing the quantity of a product that will be offered for sale at certain prices. that shows the quantity of apples that farmers would be willing to sell at different prices, regardless of demand. As you can see in Figure 1.8 "The Supply Curve", the supply curve goes in the opposite direction from the demand curve: as prices rise, the quantity of apples that farmers are willing to sell also goes up. The supply curve shows that farmers are willing to sell only a thousand pounds of apples when the price is $0.40 a pound, two thousand pounds when the price is $0.60, and three thousand pounds when the price is $0.80.
Equilibrium Price
We can now see how the market mechanism works under perfect competition. We do this by plotting both the supply curve and the demand curve on one graph, as we’ve done in Figure 1.9 "The Equilibrium Price". The point at which the two curves intersect is the equilibrium pricePrice at which buyers are willing to buy exactly the amount that sellers are willing to sell.. At this point, buyers’ demand for apples and sellers’ supply of apples is in equilibrium.
Figure 1.9 The Equilibrium Price
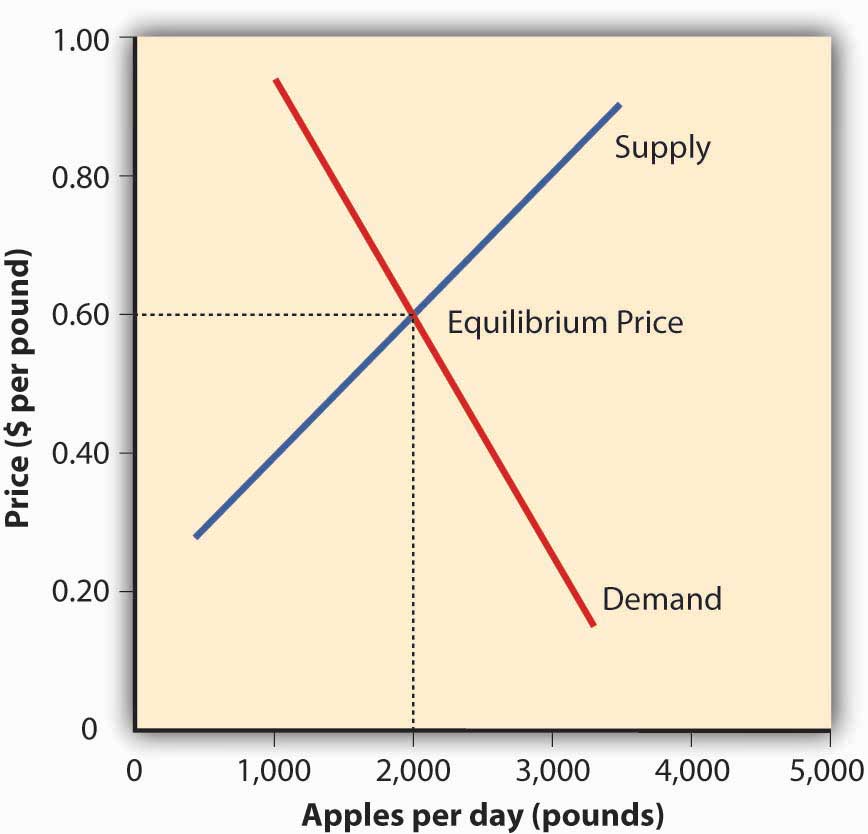
You can see in Figure 1.9 "The Equilibrium Price" that the supply and demand curves intersect at the price of $0.60 and quantity of two thousand pounds. Thus, $0.60 is the equilibrium price: at this price, the quantity of apples demanded by buyers equals the quantity of apples that farmers are willing to supply. If a farmer tries to charge more than $0.60 for a pound of apples, he won’t sell very many and his profits will go down. If, on the other hand, a farmer tries to charge less than the equilibrium price of $0.60 a pound, he will sell more apples but his profit per pound will be less than at the equilibrium price.
What have we learned in this discussion? We’ve learned that without outside influences, markets in an environment of perfect competition will arrive at an equilibrium point at which both buyers and sellers are satisfied. But we must be aware that this is a very simplistic example. Things are much more complex in the real world. For one thing, markets rarely operate without outside influences. Sometimes, sellers supply more of a product than buyers are willing to purchase; in that case, there’s a surplus. Sometimes, they don’t produce enough of a product to satisfy demand; then we have a shortage.
Circumstances also have a habit of changing. What would happen, for example, if income rose and buyers were willing to pay more for apples? The demand curve would change, resulting in an increase in equilibrium price. This outcome makes intuitive sense: as demand increases, prices will go up. What would happen if apple crops were larger than expected because of favorable weather conditions? Farmers might be willing to sell apples at lower prices. If so, the supply curve would shift, resulting in another change in equilibrium price: the increase in supply would bring down prices.
Key Takeaways
- In a free market system, buyers and sellers interact in a market to set prices.
- When the market is characterized by perfect competition, many small companies sell identical products. Because no company is large enough to control price, each simply accepts the market price. The price is determined by supply and demand.
- Supply is the quantity of a product that sellers are willing to sell at various prices.
- Demand is the quantity of a product that buyers are willing to purchase at various prices.
- The quantity of a product that people will buy depends on its price: they’ll buy more when the price is low and less when it’s high.
- Price also influences the quantity of a product that producers are willing to supply: they’ll sell more of a product when prices are high and less when they’re low.
- In a competitive market, the decisions of buyers and sellers interact until the market reaches an equilibrium price—the price at which buyers are willing to buy the same amount that sellers are willing to sell.
Exercise
(AACSB) Analysis
You just ran across three interesting statistics: (1) the world’s current supply of oil is estimated to be 1.3 trillion barrels; (2) the worldwide use of oil is thirty billion barrels a year; and (3) at this rate of consumption, we’ll run out of oil in forty-three years. Overcoming an initial sense of impending catastrophe, you remember the discussion of supply and demand in this chapter and realize that things aren’t as simple as they seem. After all, many factors affect both the supply of oil and the demand for products made from it, such as gasoline. These factors will influence when (and if) the world runs out of oil. Answer the following questions, and provide explanations for your answers:
- What’s the major factor that affects the supply of oil? (Hint: It’s the same major factor affecting the demand for oil.)
- If producers find additional oil reserves, what will happen to the price of oil?
- If producers must extract oil from more-costly wells, what will happen to the price that you pay to fill up your gas tank?
- If China’s economy continues to expand rapidly, what will happen to the price of oil?
- If drivers in the United States start favoring fuel-efficient cars over SUVs, will gas be cheaper or more expensive?
- In your opinion, will oil producers be able to supply enough oil to meet the increasing demand for oil-related products, such as gasoline?




