This is “Quadratic Formula”, section 6.2 from the book Advanced Algebra (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
6.2 Quadratic Formula
Learning Objectives
- Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula.
- Use the determinant to determine the number and type of solutions to a quadratic equation.
The Quadratic Formula
In this section, we will develop a formula that gives the solutions to any quadratic equation in standard form. To do this, we begin with a general quadratic equation in standard form and solve for x by completing the square. Here a, b, and c are real numbers and :
Determine the constant that completes the square: take the coefficient of x, divide it by 2, and then square it.
Add this to both sides of the equation to complete the square and then factor.
Solve by extracting roots.
This derivation gives us a formula that solves any quadratic equation in standard form. Given , where a, b, and c are real numbers and , the solutions can be calculated using the quadratic formulaThe formula , which gives the solutions to any quadratic equation in the standard form , where a, b, and c are real numbers and :
Example 1
Solve using the quadratic formula:
Solution:
Begin by identifying the coefficients of each term: a, b, and c.
Substitute these values into the quadratic formula and then simplify.
Separate the “plus or minus” into two equations and simplify further.
Answer: The solutions are and 5.
The previous example can be solved by factoring as follows:
Of course, if the quadratic expression factors, then it is a best practice to solve the equation by factoring. However, not all quadratic polynomials factor so easily. The quadratic formula provides us with a means to solve all quadratic equations.
Example 2
Solve using the quadratic formula:
Solution:
Begin by identifying a, b, and c.
Substitute these values into the quadratic formula.
At this point we see that and thus the fraction can be simplified further.
It is important to point out that there are two solutions here:
We may use ± to write the two solutions in a more compact form.
Answer: The solutions are
Sometimes terms are missing. When this is the case, use 0 as the coefficient.
Example 3
Solve using the quadratic formula:
Solution:
This equation is equivalent to
And we can use the following coefficients:
Substitute these values into the quadratic formula.
Since the coefficient of x was 0, we could have solved this equation by extracting the roots. As an exercise, solve it using this method and verify that the results are the same.
Answer: The solutions are
Often solutions to quadratic equations are not real.
Example 4
Solve using the quadratic formula:
Solution:
Begin by identifying a, b, and c. Here
Substitute these values into the quadratic formula and then simplify.
Check these solutions by substituting them into the original equation.
Answer: The solutions are
The equation may not be given in standard form. The general steps for using the quadratic formula are outlined in the following example.
Example 5
Solve:
Solution:
Step 1: Write the quadratic equation in standard form, with zero on one side of the equal sign.
Step 2: Identify a, b, and c for use in the quadratic formula. Here
Step 3: Substitute the appropriate values into the quadratic formula and then simplify.
Answer: The solution is
The Discriminant
If given a quadratic equation in standard form, , where a, b, and c are real numbers and , then the solutions can be calculated using the quadratic formula:
As we have seen, the solutions can be rational, irrational, or complex. We can determine the number and type of solutions by studying the discriminantThe expression inside the radical of the quadratic formula, , the expression inside the radical, If the value of this expression is negative, then the equation has two complex solutions. If the discriminant is positive, then the equation has two real solutions. And if the discriminant is 0, then the equation has one real solution, a double root.
Example 6
Determine the type and number of solutions:
Solution:
We begin by identifying a, b, and c. Here
Substitute these values into the discriminant and simplify.
Since the discriminant is negative, we conclude that there are no real solutions. They are complex.
Answer: Two complex solutions.
If we use the quadratic formula in the previous example, we find that a negative radicand introduces the imaginary unit and we are left with two complex solutions.
Note: Irrational and complex solutions of quadratic equations always appear in conjugate pairs.
Example 7
Determine the type and number of solutions:
Solution:
In this example,
Substitute these values into the discriminant and simplify.
Since the discriminant is positive, we conclude that the equation has two real solutions. Furthermore, since the discriminant is a perfect square, we obtain two rational solutions.
Answer: Two rational solutions
Because the discriminant is a perfect square, we could solve the previous quadratic equation by factoring or by using the quadratic formula.
| Solve by factoring: | Solve using the quadratic formula: |
|---|---|
Given the special condition where the discriminant is 0, we obtain only one solution, a double root.
Example 8
Determine the type and number of solutions:
Solution:
Here , , and , and we have
Since the discriminant is 0, we conclude that the equation has only one real solution, a double root.
Answer: One rational solution
Since 0 is a perfect square, we can solve the equation above by factoring.
Here is a solution that occurs twice; it is a double root.
Example 9
Determine the type and number of solutions:
Solution:
Here , , and , and we have
Since the discriminant is positive, we can conclude that the equation has two real solutions. Furthermore, since 20 is not a perfect square, both solutions are irrational.
Answer: Two irrational solutions.
If we use the quadratic formula in the previous example, we find that a positive radicand in the quadratic formula leads to two real solutions.
The two real solutions are and Note that these solutions are irrational; we can approximate the values on a calculator.
In summary, if given any quadratic equation in standard form, , where a, b, and c are real numbers and , then we have the following:
Furthermore, if the discriminant is nonnegative and a perfect square, then the solutions to the equation are rational; otherwise they are irrational. As we will see, knowing the number and type of solutions ahead of time helps us determine which method is best for solving a quadratic equation.
Try this! Determine the number and type of solutions:
Answer: Two complex solutions.
Key Takeaways
- We can use the quadratic formula to solve any quadratic equation in standard form.
- To solve any quadratic equation, we first rewrite it in standard form , substitute the appropriate coefficients into the quadratic formula, , and then simplify.
- We can determine the number and type of solutions to any quadratic equation in standard form using the discriminant, If the value of this expression is negative, then the equation has two complex solutions. If the discriminant is positive, then the equation has two real solutions. And if the discriminant is 0, then the equation has one real solution, a double root.
- We can further classify real solutions into rational or irrational numbers. If the discriminant is a perfect square, the roots are rational and the equation will factor. If the discriminant is not a perfect square, the roots are irrational.
Topic Exercises
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The height in feet reached by a baseball tossed upward at a speed of 48 feet per second from the ground is given by , where t represents time in seconds after the ball is tossed. At what time does the baseball reach 24 feet? (Round to the nearest tenth of a second.)
-
The height in feet of a projectile launched upward at a speed of 32 feet per second from a height of 64 feet is given by At what time after launch does the projectile hit the ground? (Round to the nearest tenth of a second.)
-
The profit in dollars of running an assembly line that produces custom uniforms each day is given by where t represents the number of hours the line is in operation. Determine the number of hours the assembly line should run in order to make a profit of $1,760 per day.
-
A manufacturing company has determined that the daily revenue R in thousands of dollars is given by where n represents the number of pallets of product sold. Determine the number of pallets that must be sold in order to maintain revenues at 60 thousand dollars per day.
-
The area of a rectangle is 10 square inches. If the length is 3 inches more than twice the width, then find the dimensions of the rectangle. (Round to the nearest hundredth of an inch.)
-
The area of a triangle is 2 square meters. If the base is 2 meters less than the height, then find the base and the height. (Round to the nearest hundredth of a meter.)
-
To safely use a ladder, the base should be placed about of the ladder’s length away from the wall. If a 32-foot ladder is used safely, then how high against a building does the top of the ladder reach? (Round to the nearest tenth of a foot.)
-
The length of a rectangle is twice its width. If the diagonal of the rectangle measures 10 centimeters, then find the dimensions of the rectangle. (Round to the nearest tenth of a centimeter.)
-
Assuming dry road conditions and average reaction times, the safe stopping distance in feet of a certain car is given by where x represents the speed of the car in miles per hour. Determine the safe speed of the car if you expect to stop in 50 feet. (Round to the nearest mile per hour.)
-
The width of a rectangular solid is 2.2 centimeters less than its length and the depth measures 10 centimeters.
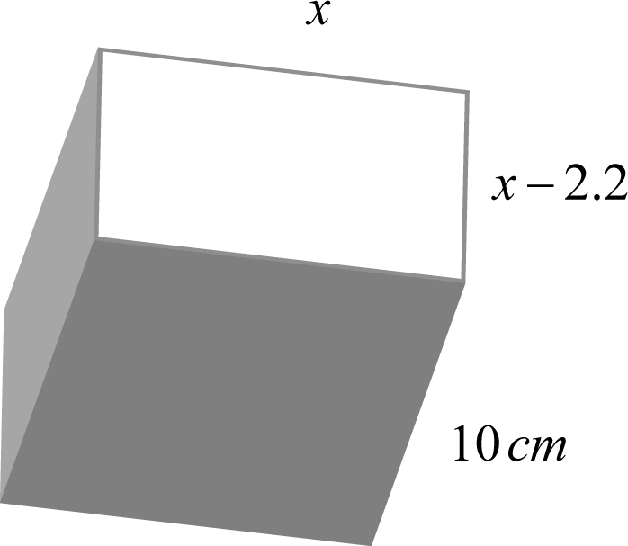
Determine the length and width if the total volume of the solid is 268.8 cubic centimeters.
-
An executive traveled 25 miles in a car and then another 30 miles on a helicopter. If the helicopter was 10 miles per hour less than twice as fast as the car and the total trip took 1 hour, then what was the average speed of the car? (Round to the nearest mile per hour.)
-
Joe can paint a typical room in 1.5 hours less time than James. If Joe and James can paint 2 rooms working together in an 8-hour shift, then how long does it take James to paint a single room? (Round to the nearest tenth of an hour.)
Part A: The Quadratic Formula
Identify the coefficients, a, b and c, used in the quadratic formula. Do not solve.
Solve by factoring and then solve using the quadratic formula. Check answers.
Solve by extracting the roots and then solve using the quadratic formula. Check answers.
Solve using the quadratic formula.
Assume p and q are nonzero integers and use the quadratic formula to solve for x.
Solve using algebra.
Part B: The Discriminant
Calculate the discriminant and use it to determine the number and type of solutions. Do not solve.
Find a nonzero integer p so that the following equations have one real solution. (Hint: If the discriminant is zero, then there will be one real solution.)
-
When talking about a quadratic equation in standard form , why is it necessary to state that ? What would happen if a is equal to zero?
-
Research and discuss the history of the quadratic formula and solutions to quadratic equations.
-
Solve for x by completing the square.
Part C: Discussion Board
Answers
-
; ;
-
-
; ;
-
-
; ;
-
-
; ;
-
-
; ;
-
-
−2, 8
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
4, 5
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
or
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.6 seconds and 2.4 seconds
-
-
12 hours
-
-
Length: 6.22 inches; width: 1.61 inches
-
-
31.0 feet
-
-
23 miles per hour
-
-
42 miles per hour
-
-
−3; two complex solutions
-
-
16; two rational solutions
-
-
25; two rational solutions
-
-
−72; two complex solutions
-
-
9; two rational solutions
-
-
−1; two complex solutions
-
-
25; two rational solutions
-
-
0; one rational solution
-
-
-
-
-
-
Answer may vary
-
-
Answer may vary




